Electronic Product Development: Ultimate Guide
16/05/2024, hardwarebee
Imagine holding the latest smartphone or wearing a cutting-edge smartwatch. These devices started as mere ideas that became essential through electronic product development. Understanding the lifecycle of these groundbreaking innovations unveils the intricate journey from conception to the consumer’s hands.
Electronic products are the heartbeat of today’s digital era, profoundly impacting how we live, work, and connect. The development of such products requires a meticulous process, blending creativity with technical expertise to meet the ever-evolving demands of the market.
This article guides you through the meticulous stages of electronic product development, highlights the collaborative efforts of the key players involved, and examines both the challenges faced and strategies employed in transforming a spark of innovation into tangible technology.
Overview of Electronic Products
In today’s technology-driven world, electronic products have become integral to our daily lives. From essential household appliances to sophisticated industrial equipment, the spectrum of electronic products is vast and multifaceted. These items, characterized by their reliance on electrical energy to perform a variety of functions, have revolutionized how we work, communicate, and entertain ourselves. The development of these products combines innovation and engineering to meet consumer demands and stay ahead of technological trends.
Definition of Electronic Products
Electronic products refer to devices that involve the flow of electrons in conductors and semiconductors. They include a wide range of commodities such as smartphones, computers, televisions, and more complex systems like medical imaging devices and navigational systems. These products are constructed using a variety of electronic components like resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits, all orchestrated to perform specific tasks or functions. The core of these products is often a circuit board that integrates the components in a precise and functional manner.
Importance of Electronic Product Development
The development of electronic products is a crucial driver of innovation and economic growth. It allows not only for the improvement of existing products in terms of efficiency and functionality but also paves the way for entirely new kinds of devices that can change the market or create new niches. Effective electronic product development can result in faster time to market, giving companies a competitive edge. Moreover, thoughtful design and development processes ensure that the product features are aligned with user needs, while also considering development costs and potential unit cost for consumers. The emphasis on electronic product development is also relevant for ensuring that products meet necessary electrical certifications and safety standards, contributing to the reliability and longevity of the products we come to rely on every day.
In this development journey, from the initial product idea to the final market launch, multiple stages like the design phase, prototyping with both electronic and plastic prototypes, and iterations based on testing are essential. Industrial designers, electrical engineers, and other stakeholders collaborate closely to create schematics, 3D models, and functional prototypes that bring abstract concepts to tangible reality. This multidisciplinary approach ultimately ensures the viability and success of the electronic hardware products in the marketplace.
Key Phases of Electronic Product Development Process
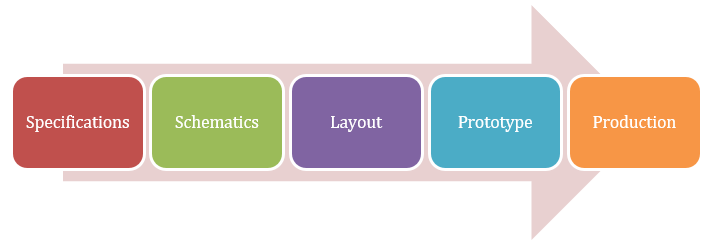
The electronic product development process is composed of several discrete stages that are crucial to the successful launch of a new product. Each phase builds upon the insights gathered from previous ones, evolving from concept to a market-ready commodity. Here are the fundamental stages of the process:
Ideation Phase
The journey of electronic product development begins with the Ideation Phase. In this early stage, creativity and visionary thinking lead the way. Team members, which often include marketers, industrial designers, and engineers, come together to generate and refine ideas. The main steps in this phase involve:
- Brainstorming: Generating a plethora of product ideas with no restrictions.
- Screening: Assessing and selecting the most promising ideas based on feasibility, market potential, and alignment with business goals.
- Concept Development: Refining the chosen product idea and outlining the desired product features, target demographics, and use cases to form a clear product concept.
Vivid brainstorming sessions and thorough market research set the foundation for a product that aims to meet consumer needs and occupy a distinctive place in the market.
Design Phase
Following the ideation phase, the Design Phase entails the transformation of a product concept into a detailed plan. It encompasses:
- Creation of Schematic Diagrams: Electronic schematics are drafted to represent the circuit connections and functions.
- 3D Modeling: Industrial designers craft a 3D computer model to visualize the physical aspects of the product.
- Selection of Components: The electronic components required for the circuit board are chosen based on performance specifications and unit cost considerations.
Attention to detail during the design phase can significantly influence the ease of manufacturing and the overall success of the product.
Development Phase
With a considerable design in place, the Development Phase focuses on bringing the electronic product to life. The essential activities in this stage include:
- Building Prototypes: Both electronic and plastic prototypes are developed, often in multiple iterations, to test the product’s functionality and design.
- Testing and Refinement: Prototypes undergo rigorous testing to identify and fix any issues. This iterative process continues until the product meets all specified requirements.
- Preparing for Manufacturing: Necessary adjustments to the design and materials are made to ensure that the product can be manufactured efficiently and cost-effectively.
The development phase is pivotal, often requiring the highest investment of time and resources, as it effectively dictates the product’s functionality and market viability.
Production Phase
In the final stage, the Production Phase, the focus shifts to manufacturing the electronic product at scale. Key aspects include:
- Finalizing the Design: Any last-minute changes based on prototype feedback are incorporated into the final design.
- Sourcing Components and Materials: Relationships with suppliers are established for the procurement of electronic components and materials.
- Manufacturing: The physical boards are assembled, soldered, and tested for quality assurance.
- Packaging and Distribution: The products are packaged, stored, and finally shipped to distribution points.
Streamlining the production phase can expedite the product’s time to market and is crucial in defining the product’s ultimate cost and quality.
These phases offer a guideline for electronic product development companies to follow and adapt based on the unique aspects of their electronic products, ensuring a structured and efficient path from concept to consumer.
Key Players in Electronic Product Development
The creation of cutting-edge electronic products requires not only brilliant ideas but also the expertise of various professionals who shepherd these concepts to fruition. Key players in this field bring together specialized know-how, creativity, and attention to regulatory standards to ensure that the developed products not only resonate with customers but are also practical to produce and compliant with industry norms. Below, we delve into the roles that these players perform, each contributing a critical piece to the electronic product development puzzle.
Engineers
Engineers are the bulwark of electronic product development. They transform the initial product concept into a tangible entity. In a typical development process, different types of engineers collaborate to bring an electronic product to life, including:
- Electrical Engineers: They are responsible for designing the electronic schematics, selecting components that yield the desired functionality within cost parameters, and developing the circuit board. Mastery in dealing with exact coordinates and the intricate layers of plastic and metal on a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is essential for these professionals.
- Software Engineers: For products requiring software interaction, software engineers develop the programming that will run either on the product itself or on the associated devices that control or enhance its functionality. This programming could range from basic firmware to complex user interfaces.
- Mechanical Engineers: They ensure that the product’s physical structure is robust, practical, and able to be produced reliably at scale. They also work closely with industrial designers to refine 3D models and prepare the product for the rigors of manufacturing.
Engineers typically create multiple prototype versions, iterating the design to achieve the best balance between functionality, manufacturability, and development costs.
Industrial Designers
The aesthetic appeal and user experience of an electronic product are in the hands of industrial designers. They play a crucial role in the Design Phase by:
- Concept Visualization: Taking product ideas and vision and translating them into visual representations that can be shared and evaluated.
- 3D Modeling: Creating the 3D computer model of the product that not only must look appealing but also function effectively and be manufacturable.
- Ergonomics and Usability: They consider how the product will be handled and interacted with, ensuring that it is user-friendly and accessible.
- Material Selection: Advising on materials for both functionality and aesthetics, including the texture and color which impact both the mold cost and the final unit cost of the product.
Industrial designers collaborate closely with engineers to refine product designs, ensuring that they are not only attractive but also functional and manufacturable.
Electrical Certifications Experts
The journey of electronic product development requires not only design expertise but also a significant understanding of compliance and safety standards. Electrical certifications experts are critical in navigating this terrain:
- Regulatory Compliance: They guide the development team through the electrical certifications necessary for market approval, identifying the relevant standards early in the development process to streamline time to market.
- Testing and Documentation: These experts manage the product’s testing phase, documenting results and ensuring that the product adheres to industry and legal standards such as the FCC, CE, RoHS, and others.
- Risk Mitigation: They help in pinpointing potential regulatory and certification risks before they become costly reworks, thus protecting the company from legal issues and market delays.
These experts provide indispensable guidance that informs the design process, helping to avoid redesigns and ensuring that the final product meets all necessary electrical certifications for its target market.
Factors Affecting Electronic Product Development
The development of an electronic product encompasses a harmonized interaction of various influences that can have significant impacts on the success and viability of the final product. These factors, which businesses must carefully balance to nurture an idea from conception to a market-ready entity, range from development timelines and costs to the availability of components and adherence to regulatory standards.
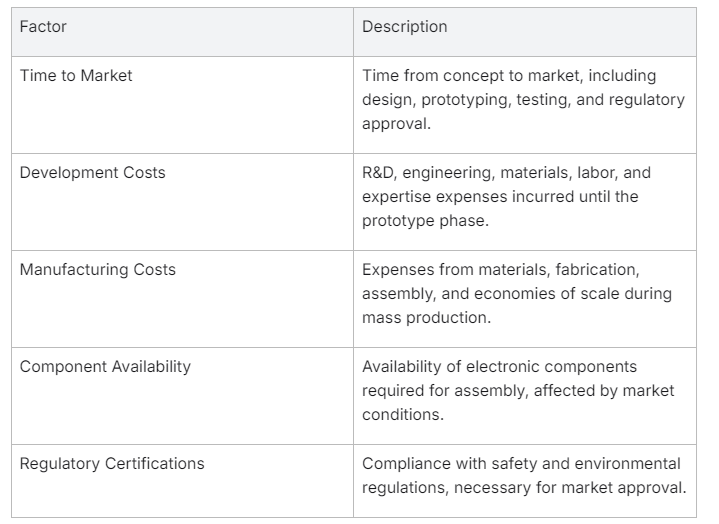
Time to Market
Bringing an electronic product to market swiftly is often a competitive necessity. An extended development timeline can result in missed opportunities and allow competitors to capture market share. Time to market is affected by the efficiency of the development process, the speed of prototyping, the rigor of testing, and the pace at which the product design receives regulatory approval. Striking the right balance between speed and thoroughness is key — rushing through these stages can incur risks, but moving too slowly can be equally disadvantageous.
Development Costs
The financial investment required to develop an electronic product can be considerable. These costs include expenses related to research and development, engineering time, prototype creation, acquiring materials for functional and plastic prototypes, electronic prototypes, and the expense of labor and expertise from electrical engineering to industrial design. Controlling development costs without compromising on quality is a central concern, as overspending can cripple a project before it even reaches the market.
Manufacturing Costs
Once the design phase is complete, the focus shifts to mass production, where manufacturing costs play a critical role. These include the unit cost of materials, mold costs for plastic components, costs of the circuit board fabrication, assembly line setup, and labor. Factors such as economies of scale, material choice, and production location have direct implications on these expenses. A well-optimized manufacturing process can significantly lower the unit cost, aiding in better market placement and profitability.
Component Availability
With the prevalence of advanced technologies in electronic products, the availability of the necessary electronic components can dictate the feasibility of production schedules. Current market conditions, such as shortages due to supply chain disruptions, can delay or increase the cost of production. Companies must have strategies to mitigate these risks, whether through strategic inventory management, alternative sourcing, or designing flexibility into their electronic hardware products to accommodate for various component options.
Regulatory Certifications
Before an electronic product reaches the hands of consumers, it must meet specific regulatory standards and receive necessary certifications. The process of electrical certifications, including FCC, CE, and RoHS, involves rigorous testing and documentation to ensure compliance with relevant safety and environmental guidelines. This stage can significantly influence the time to market and overall product to market strategy, as failure to pass these standards can lead to delays and the need for redesigns and additional testing.
Table 1: Impact Factors on Electronic Product Development
Challenges and Considerations in Electronic Product Development
Navigating through the labyrinthine process of electronic product development is fraught with challenges that can span technical intricacies, financial hurdles, legal considerations, and regulatory compliance. Successful product development hinges on addressing each of these factors adeptly. Industrial designers and engineers must often grapple with the complexity of creating a product that not only meets market demands but also remains cost-effective and legally compliant. These multidimensional challenges underscore the need for a strategic, well-rounded approach to electronic product development.
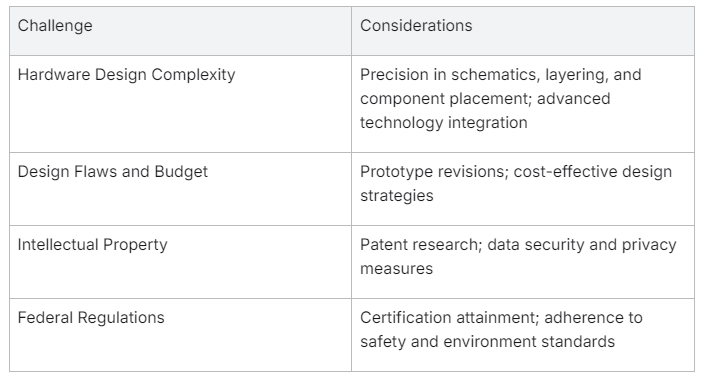
Complexity in Hardware Design
The intricacies of hardware design constitute one of the pivotal challenges in electronic product development. The task begins with translating a product concept into a schematic diagram and evolves into designing a circuit board and crafting a detailed 3D model. Each step requires precision, as the exact coordinates of components can affect the final functionality. Meanwhile, the hardware must be designed with considerations for future reproduction in mind, which includes the physical board layers and electronic components. Hardware design complexity escalates when integrating advanced technologies that demand high-level electrical engineering expertise.
Design Flaws and Budget Constraints
Mistakes in the design phase can have cascading effects, leading to functional deficiencies in prototypes and finished products. Design flaws not only compromise product features but can inflate development costs as they necessitate making repeated prototype versions, including electronic and plastic prototypes. Consequently, budget constraints play a decisive role in electronic product development. Effective cost management entails making astute decisions during the design process to optimize resources without undermining the product’s quality or performance. This tightrope walk is essential in realizing a viable product idea while aligning with financial realities.
Intellectual Property and Privacy Issues
Protecting intellectual property (IP) is a critical factor that companies must consider throughout the product development lifecycle. Ensuring that a product idea and its associated electronics design do not infringe on existing patents is a legal imperative, as is safeguarding the product’s own IP rights. Additionally, with privacy concerns escalating in the digital age, products must be designed with data security in mind, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring user privacy is protected. Navigating IP and privacy issues requires a thorough understanding of the legal landscape and often the guidance of specialized legal professionals.
Compliance with Federal Regulations
Electronic products are subject to a myriad of federal regulations intended to ensure safety, environmental friendliness, and consumer protection. Navigating these regulations is a complex aspect of bringing a product to market. From obtaining electrical certifications like FCC, CE, and RoHS to ensuring all electronic hardware products adhere to these standards, compliance can significantly affect time to market and development costs. Failure to comply can lead to costly redesigns, legal penalties, and damage to the company’s reputation. It’s essential for companies to invest in the necessary testing and documentation early in the development process to avoid such pitfalls.
Best Practices in Electronic Product Development
In the ever-evolving landscape of electronic product development, certain best practices stand out for consistently yielding successful outcomes. These practices mitigate risks, reduce time to market, and ensure product viability. From harnessing user feedback to implementing rigorous testing protocols, each practice is critical to navigating the challenging journey from product concept to market-ready electronic hardware.
Attention to User Feedback and Iterative Design
A user-centric approach to electronic product development is paramount. By paying close attention to user feedback, companies can tailor product features to better serve the target audience, enhancing user satisfaction and adoption rates. This feedback loop enables an iterative design process, where the product is continuously refined based on real-world input and testing data. Through successive prototype versions, from electronic to plastic prototypes, developers can validate assumptions and refine the product to meet user needs more closely. Iteration paves the way for a more market-oriented and consumer-friendly final product.
Collaboration between Engineering and Design Teams
The harmonious collaboration between engineering and design teams is a cornerstone of effective product development. When industrial designers work closely with electrical engineering experts, the fusion of aesthetics and functionality emerges. This interdisciplinary collaboration ensures that the schematic diagram, 3D model, and subsequent physical board and circuit board design all align seamlessly, leading to a cohesive and feasible product idea. Teams should strive for regular communication and blend their expertise to bridge the gap between conceptual design and the realities of manufacturing.
Rigorous Testing and Validation
Testing and validation are the bedrock of electronic product development, helping to ensure reliability, safety, and compliance with relevant standards. This phase demands an array of tests, from stress and performance evaluations to electrical certifications such as FCC, CE, and RoHS. By investing time and resources in rigorous testing during the design process, companies can avoid costly redesigns and mitigate the risk of product failure. Validation efforts also focus on determining whether the product meets its predetermined specifications and user expectations.
Cost Analysis and Design for Manufacture
During electronic product development, conducting a thorough cost analysis early in the design phase can be the difference between profit and loss. This includes assessing mold and unit costs, evaluating the affordability of electronic components, and determining the total expenditure of bringing the electronic product design to fruition. A Design for Manufacture (DFM) approach is instrumental, focusing on simplifying the design to reduce material and labor expenses while maintaining product integrity. By incorporating principles of DFM, companies can streamline production, avoiding unnecessary complexities and expediting time to market without sacrificing quality.
Electronic Product Development Companies
Electronic product development companies bridge the gap between a product concept and a market-ready electronic device. They specialize in transforming ideas into physical products through a meticulous design process. This process often starts with a schematic diagram, outlining the electronic components and connections, before progressing to a detailed 3D model created by industrial designers.
Key Stages of Development:
- Conceptualization: Defining product features and the overall product idea.
- Design Phase: Creating electronic product design schematics and 3D models.
- Prototyping: Building functional prototypes, including circuit boards, for testing.
- Testing and Refinement: Tweaking designs and prototype versions to ensure functionality and reliability.
To ensure a swift time to market, these companies focus on optimization in each stage, from reducing development costs to streamlining electrical engineering processes. Before a product launch, they address necessary electrical certifications and refine details like mold and unit cost to fit budget constraints.
Offerings:
- Full-cycle electronic hardware product development
- Physical board layouts and electronic prototypes, including plastic prototypes
- Exact coordinates determination for each component layer
Electronic product development companies are key partners in turning innovative electronic hardware products into commercial successes.