Introduction to RS-232 Standard
28/06/2019, hardwarebee
RS-232 stands for Recommendation Standard 232. Introduced in 1960 and used as serial ports in computer systems, the RS-232 is a set of standards that defines the characteristics and timing of the electrical signals that pass from the computer to the modem, as well as their meaning and size. The signals that pass through the port go from a computer terminal to a data communication or circuit terminating equipment such as a modem. Ever since its introduction a few decades back, it has been one of the most widely used and successful serial data transmission standards in the world. However, the use of this standard is decreasing in popularity relative to its peak years considering that newer, faster, and better standards are being designed and released periodically.
The standard was brought into existence and use by the Electrical Industries Association in the United States. It basically defined the parameters or characteristics of the signal that could be transmitted across the port from a computer to a modem. Overtime, the standard underwent multiple improvements and revisions in order to accommodate and adapt to the changes in the devices being used by the masses at a particular point in time. The goal was to incorporate the features and elements that would help the standard remain relevant to the ever evolving technology. Over the past 40 or so years, over three revisions have been introduced. One of the latest revisions is the Revision D which was issued in 1986. The one before that is titled Revision C and was issued in August of 1969. Currently, the revision that is under use is the ‘TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange’ and it was issued in 1997.
The RS-232 Standard Covers:
- The RS-232 defines the characteristics of the electrical signal transmitted across the port including the likes of the timing, signaling rate, voltage level, voltage withstand level, capacitance, as well as short circuit behavior
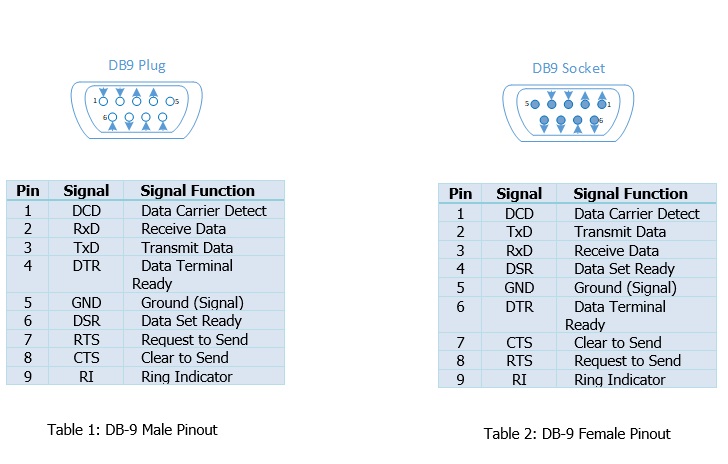
- It also defines the mechanical characteristics of the interface as well as the connectors and pin identification
- It will cover the function of each of the circuits on the interface connector
- It will also describe the standard subsets of interface circuits for selected telecom applications
RS-232 Applications
When it was first introduced, the RS-232 standard was only meant to allow a connection and data communication between a computer terminal and a modem. Now, however, we observe that this standard is being used across the board for multiple applications and purposes. It has been used to connect devices such as printers and other hardware. Its use became especially prevalent and widespread with the introduction of Personal Computers. Most PCs, you will find, will already have an RS 232 serial port regardless of whether or not you are looking for one in your system.
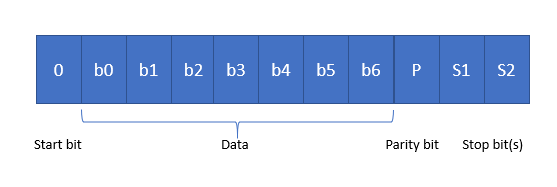
Figure 1: RS-232 transition frame
Despite now having decreased use in personal computers as is explained below, RS 232 ports are still preferred and widely used in scientific instruments as well as industrial level machinery and equipment where all that the network system needs is a short range low speed wire connection to transmit some data.
RS-232 Drawbacks
While it may be one of the most popular choices due to its easy use and availability, there are also a few disadvantages associated with the use of this protocol. To begin with, the RS-232 standard allows for only a very limited cable length to be used as defined by its specifications. This length is topped off at a maximum of 50 feet, going beyond which is not recommended.
On another note, as you may have noticed, RS-232 is a single ended standard, meaning there is only one route using which signals are sent as well as received. This may directly translate into interference between signals and unnecessary noise production.
Another one of the downsides is that you will find that you can only connect one device per serial port, meaning you cannot delve in multi-point usage and multi drops.
When it comes to comparing the parameters and characteristics of the RS-232 standard with that of other standards such as the RS-422, RS-485, and the Ethernet, the former also has relatively slower transmission speeds, shorter cable lengths, as well as larger voltage swings.
Due to the larger voltage swings, the standard tends to increase the power consumption across the interface and limits the speed of the network.
Because of the disadvantages that are associated with the use of RS-232 standard serial ports, we have mostly switched to USB ports which is why the incidence of coming across an RS-232 port in a newer computer system is becoming more and more rare. As such, if you have a device that follows the RS232 standard and wish to connect it to your computer that does not have an inbuilt RS-232 port, you will have to find yourself an external USB to RS-232 converter or an internal expansion card with a serial port.