Introduction to SPI Interface and Protocol
29/12/2019, hardwarebee
SPI stands for Serial Peripheral Interface. Developed by Motorola in the 1980s, SPI protocol is now a specification standard for short distance communication especially in embedded systems.
How Does SPI Protocol Work?
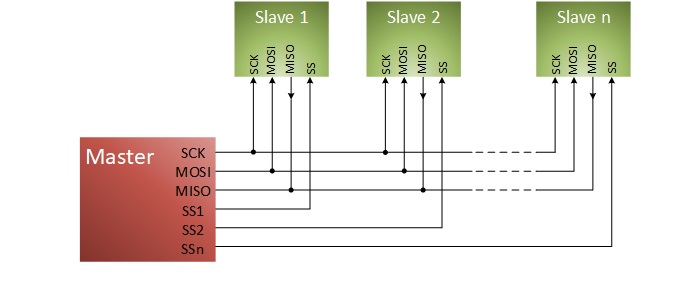
The SPI architecture is a typical master slave structure having a single master and communicating with the connected devices in full duplex. The master device is what gives the frame for reading and writing purposes whereas the slave devices are supported with the help of the slave select or the chip select lines. In the case that only one slave device is being used, it is possible to attach the slave select pin to the logic low if permitted by the slave. In the case that multiple slave devices are being used, each slave device will require an independent slave select signal from the master device in order to operate.
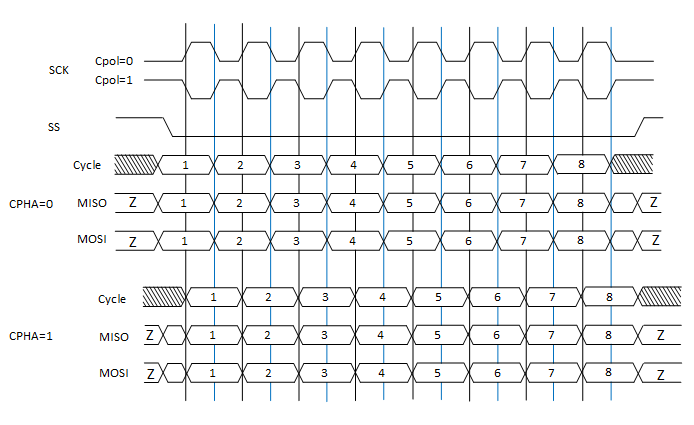
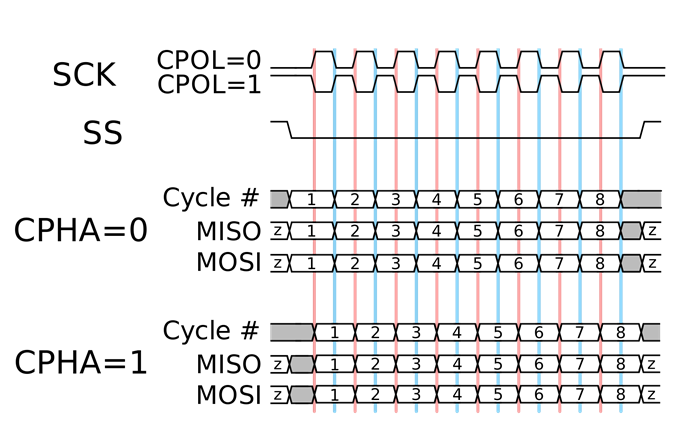
The master starts with selecting the slave device that is the target for the data transfer (either read or write cycles). The clock cycle is then issued, only after the master device has waited out any time that may be required for tasks such as analog to digital conversion. Apart from setting the clock frequency, the master device is also responsible for setting the clock polarity (CPOL) and phase (CPHA). During the data transmission process, the master sends a bit of data on the MOSI line which is the Master Output Slave Input or Master Out Slave In line (meaning the master device is giving the output of data) and reads it as well. If a certain slave device does not receive an activation signal on its chip select line, the input clock must be ignored by that slave and it should not respond to the MISO signal. Sometimes, there may be a need to implement an external tristate buffer to ensure this.
Two shift registers are involved in the data transmission process, one each placed with the master and the slave device respectively. Register bits are continually shifted out and in until the master and the slave device have essentially exchanged the register values since the registers are connected in a virtual ring topology. In the case that more data needs to be transmitted and the cycles need to continue, the shift registers return to their original values or locations and the process repeats once again or however many times as needed for the complete transmission of the intended data. Typically, eight-bit words are used for the transmission of data in an SPI but variations have been observed in the word size with digital to analog and analog to digital converter using twelve bit word sizes, and touch screen controlling devices and audio codecs using sixteen bit word sizes.
Slave vs. Daisy Chain Configuration in SPI
Conventionally, SPI is used in an independent slave configuration but some applications require the use of the daisy chain configuration. In the independent slave configuration, an independent chip or slave select line is present for each of the slave devices. This means that the master is only able to control or activate one slave at any given time. In a daisy chain configuration, on the other hand, the first slave output is connected to the second slave output and the chain continues on with the number of slaves attached to the master in the system. This means that when the second pulse of clock signals goes out, each of the SPI ports also sends along a copy of the first clock signals as well. This essentially creates a communication shift register.
SPI Applications
SPIs are frequently used in embedded systems for examples: Secure Digital cards, LCDs interface, A2D or D2A interfaces. They are used in embedded systems since they give great savings. They are used across a variety of different applications such as in FLASH and EEPROM memories, real time clocks, communications chips such as Ethernet and USB, audio codecs, SD cards, and a number of different kinds of sensors such as temperature and pressure, among others.
SPI Advantages
There are a number of features that make SPI the best choice for many applications.
- SPI has great signal integrity and operates at high speeds thanks to the push pull drivers instead of the conventional open drain system.
- In terms of the data transfer, there is a lot of freedom and flexibility in terms of bits transferred and message specifications.
- The hardware normally does not take up too much power because of less circuitry, no failure modes are associated with it, there is no need for precision oscillators since the slaves use the clock of the master, and there is no need for transceivers either.
- The default version of the protocol uses full duplex mode communication.
- Unidirectional signals.
- Only four pins on the IC packages are used.
SPI Disadvantages
Unfortunately, it is not all paradise in the world of SPI and there are still a number of issues that need to be addressed.
- Needs even more pins as compared to I2C.
- The slave is unable to give any hardware flow control.
- There is no acknowledgement of the hardware of the slave device, meaning its loss is not detected by the master.
- In the case of a shred bus, you would need out of band chip select signals since there is no in band addressing.
- There is no currently described error checking protocol making the process error prone.
- Is limited to handling extremely short distances only, especially when compared to some of the other standards such as RS-232 or CAN-bus.