Understanding Ballast Resistor
12/05/2022, hardwarebee
A ballast resistor is a resistor that resistance increases as current flows through it is increases and its resistance reduces as current flows through it drops. As a result, a device that helps to preserve the electrical circuit’s stability. Even if there are variations in the applied voltage or the rest of the circuit, the ballast resistor maintains a constant current flow through it. The ballast effect is achieved by using a resistive substance that increases resistance as the temperature rises. These resistors are used to adjust for fluctuations in line voltage, as well as the negative volt-ampere characteristics of other devices such as vapor lamps, fluorescent bulbs and in various vehicle ignition systems. The purpose of this article is to provide an overview of a ballast resistor and how it works and what are the applications.
A ballast resistor is an electrical and electronic component that controls the flow of current in a circuit. When the flow of current through it increases, the resistance of ballast resistor increases, and when the flow of current reduces, the resistance decreases. The ballast resistor keeps the current flowing steadily throughout the circuit, even if the applied voltage fluctuates. This resistor serves as a variable load on the system, as opposed to load resistors, which have a constant resistance. In general, the components connected in series with the ballast resistor to get the same current, and ballast resistors are frequently linked in series through the negative load. Series resistors are used in certain ballasts, whereas capacitors and other complicated components are used in others. Below is a schematic of a ballast resistor.

Figure 1: Symbol of Ballast Resistance
Types of Ballast Resistor
There are two types of ballast resistors: fixed ballast resistors and self-variable ballast resistors
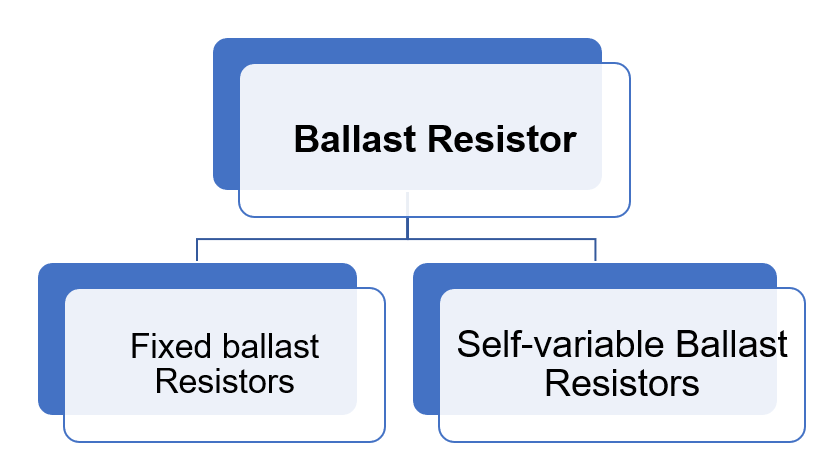
Figure 2: Ballast resistors types
Fixed ballast Resistors
A ballast resistors which have fixed resistance included in this category. For a wide range of applications, a high resistance value is desirable. Simple circuits with low-power demands, such as neon or LED bulbs, often use this sort of ballast resistor. This fixed resistor can also be used to control the ventilation fan speed. The ballast resistor has two center taps and is a fixed resistance. The fan speed selection switch bypasses parts of the ballast, resulting in complete speed selection of the whole ballast resistor and no low speed option.
Self-variable Ballast Resistors
These ballast resistors have the ability to modify resistance in response to current variations. An increase in current, for example, will increase resistance, whereas a drop in current will decrease resistance. These ballast resistors are often used in incandescent lights. As the current through the lamp grows, the ballast resistor warms up, and the resistance climbs with the rising temperature, increasing the voltage drop across the resistor. The temperature of the ballast resistor reduces when the current is lowered, as does its resistance, and thus the voltage drops.
This type of ballast resistor has an advantage over a suitable fixed resistor in that it enables for more precise current regulation. Another benefit is that, as compared to a fixed resistor, the power lost in the resistive ballast is minimized since the ballast loses a smaller percentage of the overall power.
Working of Ballast Resistor
The ballast resistor functions in such a way that as the current flowing through it increases, so does the temperature. As a result of the rise in temperature, the resistance will rise. As a result, increases in resistance will impede current flow across the network. These resistors are used in autos to start the engine. The resistor limits voltage depletion from the battery after the motor starter starts the automobile engine. It may also be used in lighting-related applications such as LEDs, neon lights, fluorescent lamps, and so on.
Ways to Test a Ballast Resistor
In automotive applications, the ballast resistor is utilized to lower the ignition coil’s voltage level. To test the ballast resistor in automotive applications an ohmmeter and a multimeter to is needed.
If the ignition coil is not linked to the ballast resistor, the ignition coil receives the entire supply voltage. The battery is usually utilized to power the ignition system. The battery voltage will most likely be 12V or 24V in most circumstances. If the voltage level decreased to 7-8V after connecting the ballast resistor, then the ballast resistor will be in good condition. However, if the voltage level of the ignition coil will be high it means the ballast is damaged. So, to extend the life of the ignition coil we need to lower the voltage and for this purpose we connect a ballast resistor to the ignition coil to decrease the voltage.
Uses of a Ballast Resistor in Real Life Application
In an electrical system, a ballast resistor serves to control current and voltage. It protects equipment against overcurrent and overvoltage problems. Ballast resistors are mostly utilized in lighting and automotive applications.
Ballast Resistor in a LED Circuit
The LED bulb may be damaged if the source voltage in an LED circuit is higher than the rated voltage of the LED bulb. To avoid this, a ballast resistor should be connected in series with the bulb. The voltage across the LED is decreased to a safe level by connecting the ballast resistor in this manner. The figure below shows a circuit schematic for the same.
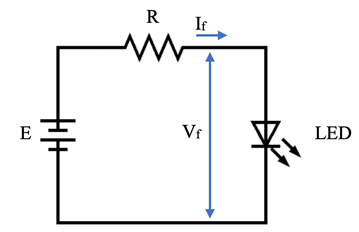
Figure 3: Ballast Resistor in a LED Circuit
The values of ballast resistance can be calculated as:
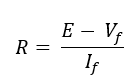
Where, R is the ballast resistor’s resistance, E stands for voltage source, Vf is the LED’s forward voltage, while If is the LED’s forward current.
Let’s suppose we have a 4-volt LED with a 10-mA forward current and a 10-volt supply source. This means that the voltage across the LED must be 4 volts or less. As a consequence, the resistance of the ballast resistor should be R= (10-4)/0.010 = 600 ohms.
Ballast Resistor in Fluorescent Lamps
Fluorescent lighting is a popular and efficient lighting solution. This form of lighting system, however, has a disadvantage. When directly connected to the voltage source, it heats up quickly. This occurs as a result of the lamp’s uncontrolled current demand as soon as it is turned on. A ballast resistor is utilized in the circuit, which is connected in series with the bulb, to prevent overheating owing to the high current draw. So, the purpose of a ballast resistor is just decreasing the voltage and controls the current.
The lamp, on the other hand, must create an arc between its two electrodes in order to light up. This requires a high starting voltage that is approximately equal to the supply voltage. After the arc is formed, the ballast resistor provides the needed voltage during start-up and then reduces the voltage while managing the current flow. In the diagram below, a fluorescent light tube is connected to a ballast resistor and a starting switch.
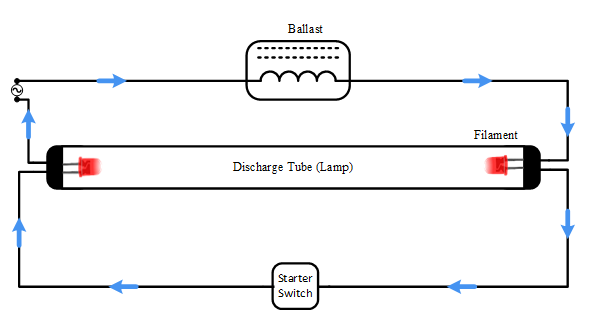
Figure 4: Ballast Resistor in Fluorescent Lamps
Automotive Ballast Resistor
In automotive machinery, such as vehicle engines, ballast resistors are widely used in ignition kits. Because of their use, such devices are called as Ignition Ballast Resistor. The usage of this device reduces the chances of coil failure. It connects the primary voltage source of the ignition coil to the coil stud. This reduces coil voltage and current, ensuring that the coil does not overheat as a result of the addition. To start the engine, however, a high voltage equivalent to the primary power source is necessary. As a result, a jumper wire is usually used to connect the ballast resistor. The voltage necessary to start the engine is supplied by this jumper wire.
Some Other Applications of Ballast Resistor
- The majority of these resistors are utilized in lighting and automotive applications.
- These resistors assist to keep battery draining and overloads at bay by controlling the flow of electricity in an electrical system.
- This resistor is used in a battery ignition system to adjust the main current by connecting it in series through the primary winding.
- These are used to compensate for changes in line voltage in vapor lamps and laser circuits.
- LED circuits, fluorescent lights, and automotive applications all employ these resistors.
- The ballast in the HeNe laser is used to stabilize the tube current and limit it. As a result, the typical ballast resistance for most HeNe lasers is around 75 K.
- These are found in low-power devices such as LEDs and neon lights.
- Because they have low-powered loads, this resistor is mainly utilized in basic circuits.
Advantages
The following are some of the benefits of using a ballast resistor:
- These resistors assist in the regulation of voltage and current in electrical systems.
- This resistor safeguards the equipment from overvoltage and overcurrent.
- In the rest of an electric circuit, these resistors diminish variations in current and applied voltage.
- As a result, a ballast resistor is mostly utilized for over-voltage, current, or protection inside various automobile and light circuits in order to provide circuit stability.