What is Embedded Software?
26/04/2021, hardwarebee
What is embedded software? embedded software refers to a piece of software embedded in a non-PC device. The software is written to control the specific functions of the device that it runs on and it is therefore designed to work within the constraints of the device. The following diagram can help answering the question “what is embedded software?”
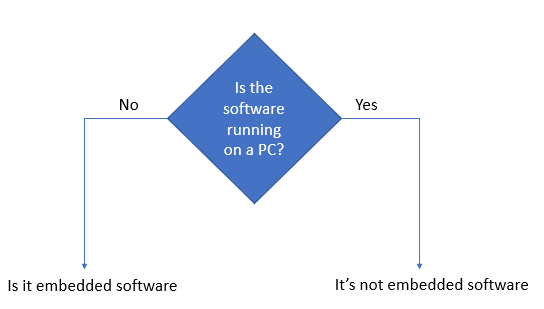
Figure 1: What is Embedded Software?
Embedded Software vs Firmware
Embedded software is very similar to firmware and they are both used on the same device. However, firmware is a special type of embedded software that is programmed on to a nonvolatile memory like EPROM or ROM, meaning it cannot be modified, and it is used for booting or running the device. All firmware is embedded software but not all embedded software is firmware.
In contrast, the work of embedded software is to control the overall operation of the hardware.
Firmware is essentially developed along with the hardware (chip) so that it can optimize the operations in terms of speed, security and power consumption while embedded software is developed to enable the hardware to meet the needs of the overall product or system.
Embedded Software Examples
Embedded software can be as simple as the one used in controlling home lighting that runs on an 8-bit microcontroller requiring just a few kilobytes of memory or as complicated or the one used in aircraft avionics systems.
Examples of common embedded software use cases include factory robots, WiFi-routers, TV, PlayStation, wireless Speakers, GPS devices, calculators, etc.
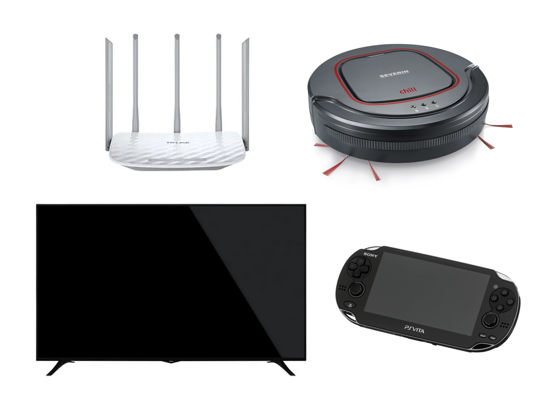

Figure 2: Examples of Products using Embedded Software
Characteristics and Features of Embedded Software
Firstly, embedded software is designed for specific tasks, unlike the general-purpose computers that handle multiple tasks. The hardware components (e.g. chips) within a device that house the embedded software are called embedded systems. Embedded software is what gives the embedded systems their features.
Embedded systems are not stand-alone devices but rather small components within a larger device like a robot or smart car. For example, while the general purpose of the robot vacuum cleaner is to clean the floor, it consists of an embedded system (CPU/SoC and chips) with embedded software that is responsible for running the cleaning process.
In the last decade where SoC (System on Chip) was introduced, the embedded software is running on the SoC because it including a CPU inside (as opposed to an external dedicated CPU chip). Read more about SoC here.
Some of the key characteristics of these embedded systems include:
- Being task-specific – They are designed to do the same task continuously for their lifetime. If it is an embedded system for a robot vacuum cleaning, for example, that embedded system will only function to vacuum cleaning for its lifetime without changing its function.
- They perform tasks within a specified time frame – am embedded systems is created to perform the assigned task within a certain time frame and therefore it has to be flexible to perform fast enough when required to do so. For example, an embedded system in a car braking system must perform within the required timeframe and failure to which an accident would be caused. This feature is often called Real Time operation.
- They rarely use a user interface (UI) – operations are preprogrammed and therefore most embedded systems do not require human input along the way. They are set to obtain inputs from the tasks they are performing to determine the next cause of action.
- Embedded systems are small-sized and they use little power. They are also designed to achieve certain efficiencies.
- They are designed using microprocessors or microcontrollers. The software is running on these devices.
- They require connection to peripherals to connect to external input and output devices.
Embedded systems are classified using two methods; based on their functional requirements and performance and based their complexity. There are four groups of embedded systems based on the functional requirements and performance and these include:
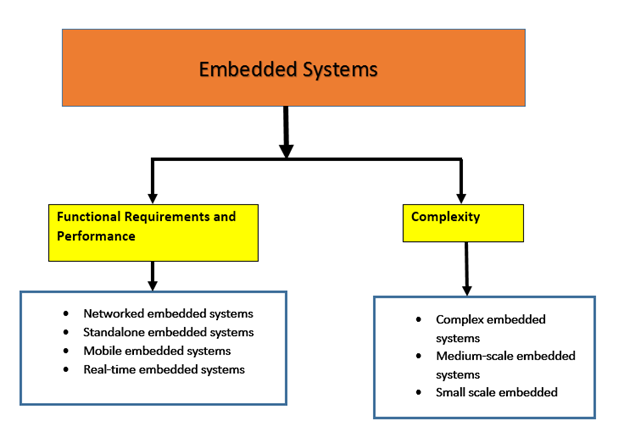
Figure 3: Types of embedded systems
- Networked embedded systems – They require connection to a network to perform their tasks. An example is a home security system.
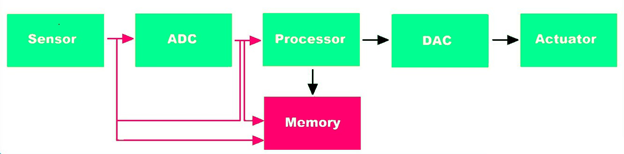
Figure 4: Embedded system circuit for a home security system
- Standalone embedded systems – They perform tasks on themselves without the need for an external processor. Examples include washing machines, mp3 players, and digital cameras among others.
- Mobile embedded systems – They are found in small portable devices and they are therefore highly constrained. Examples include calculators and mobile phones.
- Real-time embedded systems – They complete their specified tasks within a specified time. Examples include industrial robots, telephone communication devices, radio communication devices, patient monitoring systems, and traffic control systems among others.
On the other hand, there are three groups of embedded systems based on their complexity and these include:
- Complex embedded systems – These are embedded systems that use 32-bit or 64-bit microprocessors and can perform large scale tasks
- Medium-scale embedded systems – These are embedded processors that use 16-bit or 32-bit processors
- Small scale embedded systems – These are embedded systems that use 8-bit or 16-bit processors. They are used in washing machines, automatic door locks, ovens, etc.
History of Embedded Software
The first embedded system was developed by Charles Start Draper in 1960 at MIT for the Apollo Guidance System. The purpose of developing the embedded system was to reduce the size and weight of the project.
Later, Autonetics developed an upgraded embedded system in 1965 by developing the D-17B computer that was used for the Minuteman missile guidance system.
Later on, the first embedded system for a vehicle was developed in 1968 before the first microcontroller was developed by Texas Instruments in 1971.
Then in 1987, Wind River developed the first embedded operating system (OS) that was called VxWorks. In 1996 Microsoft Windows developed the CE embedded system before Linux also developed its embedded system.
Difference between Embedded Software and Regular Software
Embedded software is very different from application software, which is the regular type of software known to common users. The former runs on a non-PC device and serves as the operating system (OS), the latter controls the operations of a computer and runs on top of an actual operating system.
By virtual of the fact that the hardware or device where the embedded software run on have limited capabilities compared to PCs, embedded software is restricted to the devices specifications and any additions and updates are highly controlled. But on the other hand, application software has fewer restrictions because of the large number of resources.
Embedded Software Development Tools
The following tools are used in developing embedded software:
- Compilers
- Assemblers
- In-circuit emulators or debuggers
- Math workbenches for simulating the mathematical aspects of embedded software meant for digital signal processing
- System-level modelling and simulation tools
- Modelling and code generating tools
- Development boards
Embedded Software Operating Systems
The operating systems used in embedded software, commonly referred to as embedded operating systems can be categorized into five categories namely:
- Single System Control Loop operating system – These types of OS is designed to only run a single task
- Multi-Tasking Operating System – These types of OS handles multiple tasks and processes operating simultaneously
- Rate Monotonic Operating System – These operating systems are designed to ensure that the task runs take specific time intervals and run for specific periods
- Preemptive Operating System – These are types of multitasking OS that runs higher priority tasks before lower priority tasks instead of running them simultaneously.
- Real-Time Operating System – These OS process data as it comes in in real-time. Examples include the VxWorks, the Microkernels, RTLinux, pSOS, VRTX, and QNX.
Embedded Software Programming Languages
Embedded software is commonly written in either C or C++ programming language. However, other high-level programming languages are also used in writing embedded software and these include:
- Python
- JavaScript
- Ada
Embedded Software Today & Future
Today the biggest part of an embedded software code is dedicated to timing issues or thread, messages and event management leaving a very small part of the code to take care of the actual application. Also, it is extremely difficult for an application developer to write embedded software for several networked embedded devices without extensive knowledge in embedded software and networking.
Moving into the future new design environments and operating systems will be required to provide a mental model that is more advanced and yet very simple to use. An example of such a framework is the PIECES framework that allows application developers to use a state-centric model of programming to write the embedded software for an application to be used for sensor network signal processing and tracking.
But notwithstanding, Embedded software is a growing industry and its market surpass $140 billion in 2013 and projected to hit $400 billion by 2035.







