Unit Of Resistance
07/11/2022, hardwarebee
What is resistance?
In electronics, the term “resistance” is the fundamental property of every electronic device. Resistors are a common element in electrical and electronic devices.
Even a small piece of wire has some resistance. When an electron flows through devices and wires, it encounters some hindrances in its path. This is because of collisions with atoms in the conducting materials. The collisions of moving electrons with other atoms and molecules result in the production of heat. As a result, anytime a current travels through a conductor, the conductor generates heat, which needs to be completely dissipated.
Free electrons move through the conductor under the influence of an electric field. They collide with each other and other atoms as well. Because of these constant collisions, there is resistance in the flow of electrons.
Resistance, as the name implies, is the opposition to the flow of something. In electrical and electronics engineering, resistance is a measure of opposition to the flow of current.
Compared to two pieces of material of the same length and dimensions, one is a metal (like copper wire), and the other is an insulator (like rubber). A metal may have a resistance value of less than an ohm, while an insulator may have a resistance value of several thousand ohms.
Resistors are the components used to describe the term resistance in an electronic circuit and have a stated value of resistance. All the numerical values used to describe physical quantities must have a unit of measurement as well. The unit of measurement is the Ohm, named after George Ohm, a German physicist. The standard symbol is “R.” If a certain component has a resistance of 1000, it is better to write it as R=1000 ohm or R=1000Ω or R=1kΩ
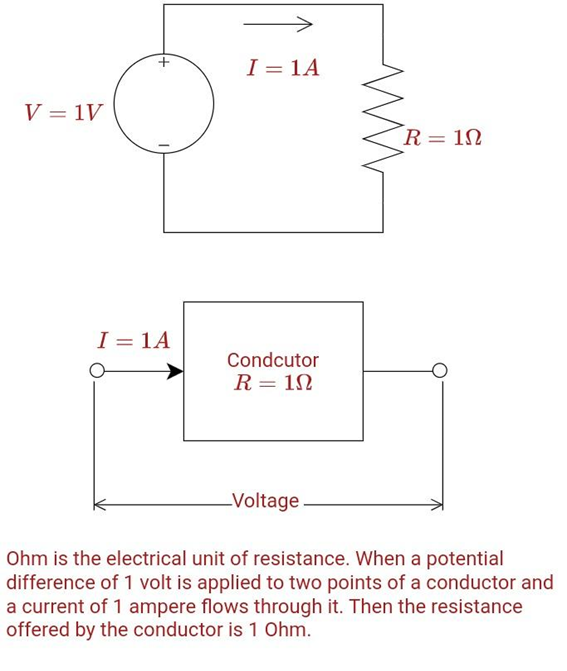
Figure 1: Definition of 1 Ohm
The Definition of 1 Ohm
“Ohm” is the electrical unit of resistance. When a potential difference of 1 volt is applied to two points of a conductor and a current of 1 ampere flows through it, Then the resistance offered by the conductor is 1 ohm.
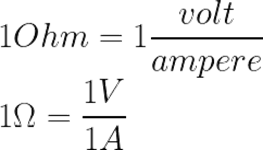
![]()
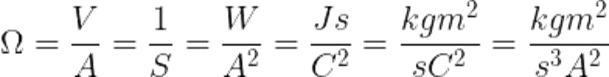
Dependence of Resistance
The resistance of a material depends on its material and composition. It also depends on temperature and physical dimensions (geometry of the wire). The resistance (R) of the conductor at 20 °C can be calculated with the help of this formula.
![]()
Where,
- A is the area of cross-section
- L is the length of the wire
- ρ is the resistivity
Resistivity
The definition of resistivity is given below:
“The resistivity of a substance is the resistance of a cube of that substance having edges of unit length, with the understanding that the current flows normal to opposite faces and is distributed uniformly over them.”
It is a fundamental physical property of all materials. It helps in the comparison of two conductors, like how different materials allow or resist current flow. When two wires have the same dimensions but different materials, they have different resistance values.
The temperature has an inverse relationship with it. The higher the resistivity, the higher the resistance will be. Every material has a different resistivity value, which depends on temperature. It assumes that it remains constant. It is symbolized by the Greek letter ρ(rho) and the units are Ω·m.
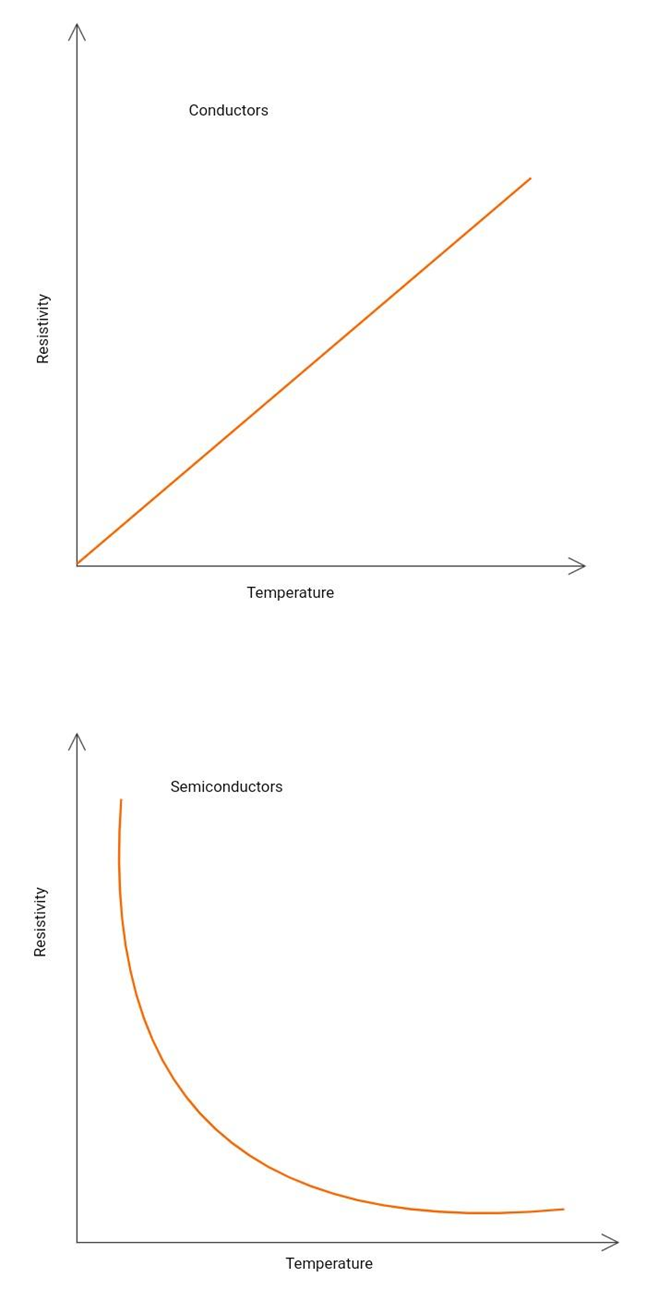
Figure 2: Resistivity and temperature graph (for conductors and semiconductors)
Length of Resistance
The larger the resistance, the greater the opposition to the flow of current. The larger the conductance, the greater the flow of current through the material. The longer the path the current has to travel across the resistor, the greater the resistance will be. The length is the dimension that is parallel to the electric field. When evaluating resistance, physical dimensions should be carefully analyzed with respect to the electric field. Refer to the figure 3 below.
Have a look at case 1. In this case resistance between point A and point B of the conductor is required. The electric field is applied between these two points. The current flows from point A towards point B. The distance covered by electrons is equal to the length of the conductor that is 10cm. The area in this case is 25cm2.
Have a look at case 2. In this case resistance between point C and point D of the conductor is required. The electric field is applied between these two points. The current flows from point C towards point D. The distance covered by electrons is equal to the length of the conductor that is 5 cm. The area in this case is 50cm2. In this case length is shorter and area is larger and hence the resistance value is lower in this case.
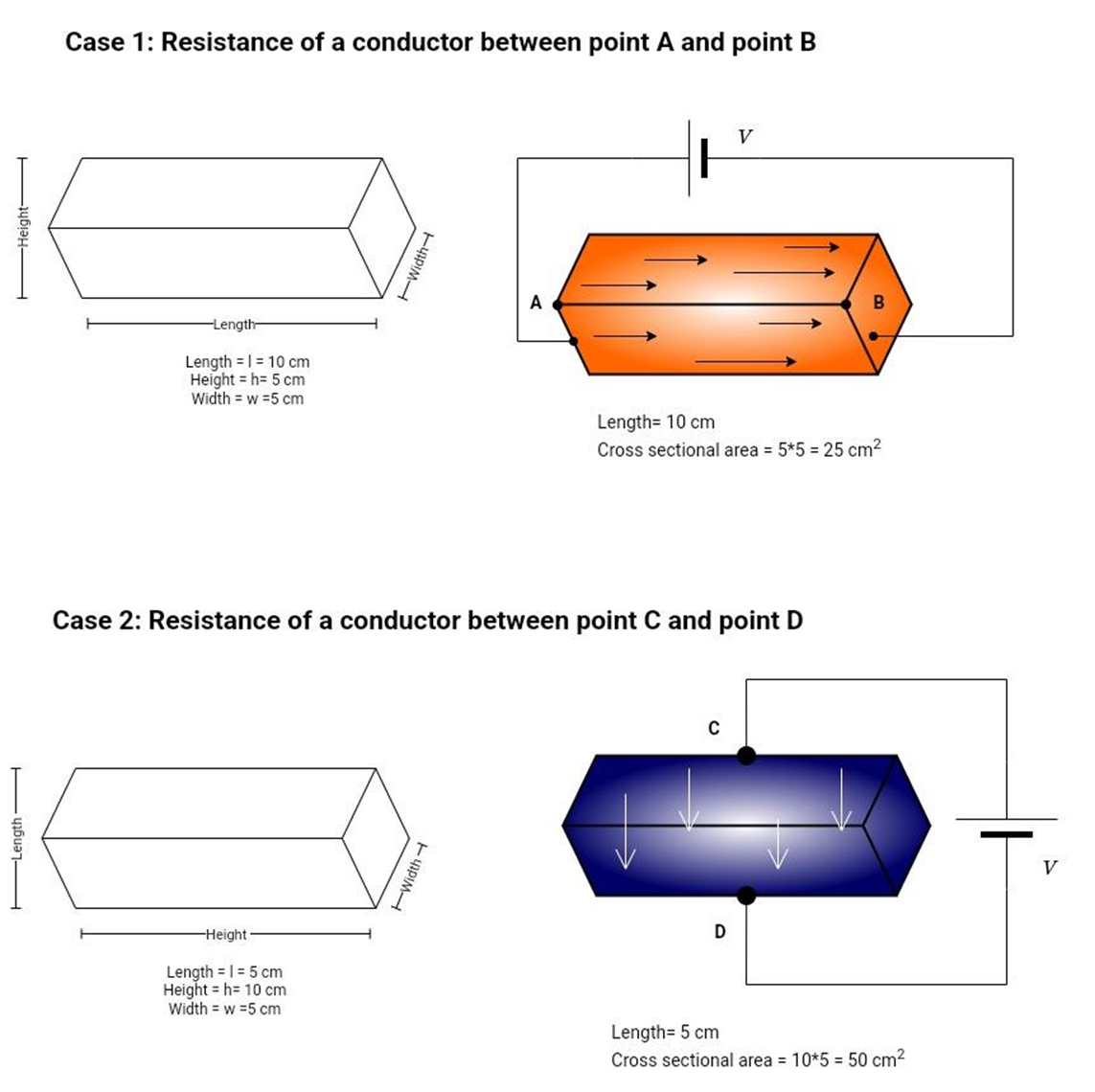
Figure 3: Direction of electric field and resistance
Area
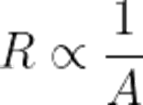
It is clear from the above expression that resistance is inversely proportional to the area. If the cross-sectional area is doubled, then the resistance of the wire is reduced by half. Have a look at the
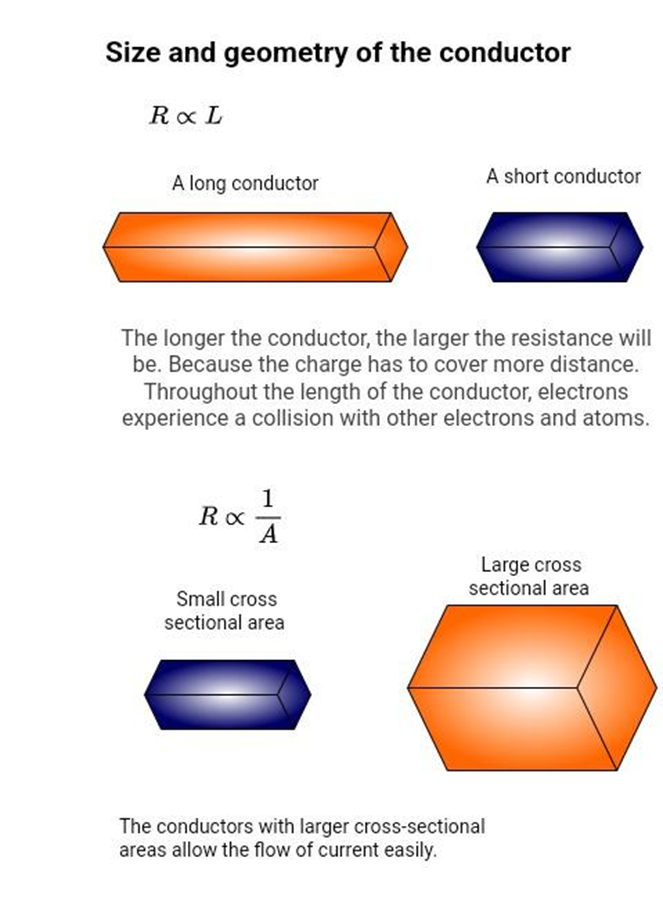
Figure 4: Resistance depends on physical dimensions of the conductor
Temperature of Resistance
The resistance of a material depends on temperature because of the number of collisions between electrons and atoms in the material. With the increasing temperature, the number of collisions also increases. There is a slight increase in resistance to the flow of current.
The relationship between resistance and temperature is known as the temperature coefficient of resistance. It is mainly dependent on the material. Most conductors have positive temperature coefficients. It means that as the temperature of a conductor increases, resistance also increases. Some materials have negative temperature coefficients as well. With increasing temperature, the resistance of the material decreases. In some materials, like semiconductors, an increase in temperature will result in thermally generated charge carriers. Increased charge carriers will result in decreased resistance.
- For conductors resistance (and resistivity) increases with an increase in temperature.
- For semiconductors resistance(and resistivity) decreases with an increase in temperature.
Resistance and Ohm’s Law
It is the fundamental law of electricity. It describes the relationship between voltage and the current flowing through the conductor. Ohm’s law defines resistance in terms of voltage and current relationships.
According to Ohm’s law;
“Voltage across the conducting material is directly proportional to the current flowing through it.”
Mathematically;
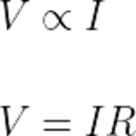
Where,
R is the constant of proportionality, also known as the resistance of the material. So, the resistance of a conductor is the ratio of the potential difference between the two ends of a conductor and the current flowing through it. Not all materials obey Ohm’s law. This law holds true for linear resistors. Linear resistors have constant resistance and their current-voltage characteristic curve is a straight line passing through the origin.
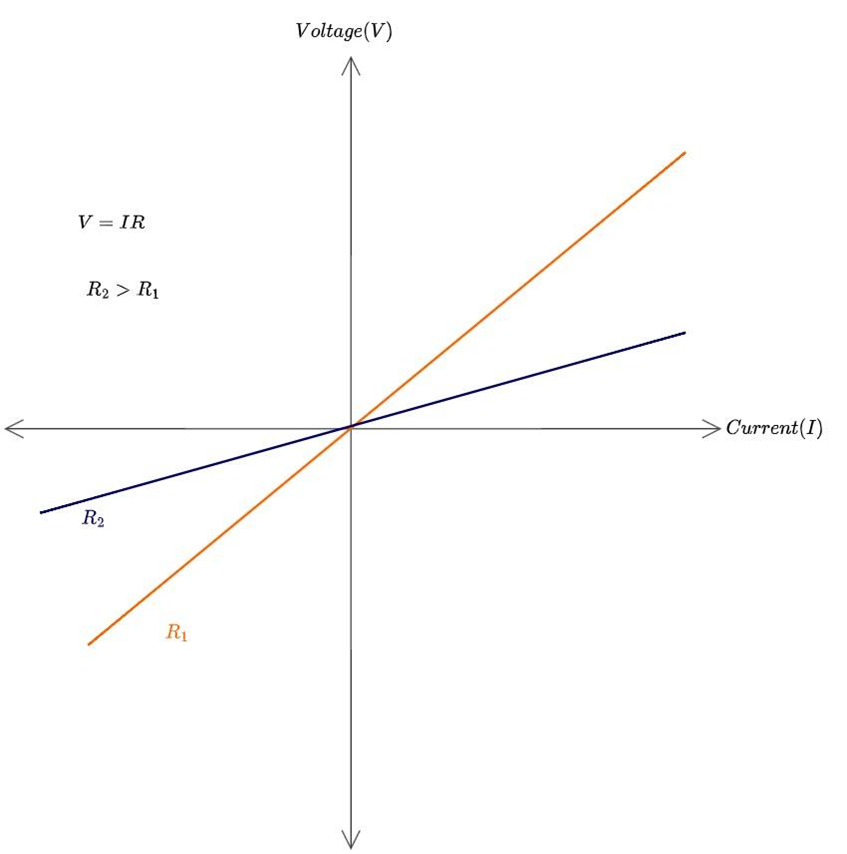
Figure 5: Ohm’s Law
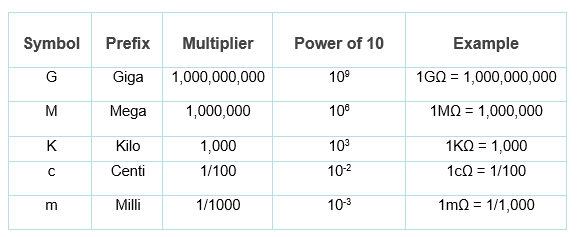
Unit of resistance conversion table (Ohm Converter):
During mathematical calculations and analysis, most of the measured quantities are very large or very small. It is better to represent it in scientific notation. It is a convenient way of writing numbers that are too large or too small in decimal form. The majority of time units of resistance must be converted into scientific notation.
For example,
1000Ω = 1KΩ
5600Ω = 5.6KΩ
780,000Ω = 780KΩ = 0.78MΩ
440,000,000 = 440MΩ
Applications
In electrical and electronics engineering, this tiny passive component is one of the key components. Some uses are given below.
- To limit the flow of current (current limiting and current division)
- Setting time constant
- In temperature sensors
- To divide voltages
- Heating applications
- Gain control
- To bias active elements