Electronics Manufacturing Services: Ultimate Guide
20/05/2024, hardwarebee
In an age dominated by technology, electronics manufacturing services (EMS) play a pivotal role in turning innovative designs into usable devices. At its core, EMS acts as the backbone of the entire electronics industry, shaping the efficiency and quality of our everyday gadgets. For tech enthusiasts and industry stakeholders alike, understanding EMS is crucial to appreciating how our smartphones, laptops, and medical devices transition from blueprints to tangible products.
The history of EMS reveals the metamorphosis of a sector that has streamlined the production of electronic components and assembled final products for decades. From humble beginnings to becoming integral partners of major tech brands, the rise of EMS companies offers a fascinating insight into the evolution of modern manufacturing. This complex journey not only mirrors technological advancements but also the shifting landscapes of global industry.
Embarking further into this exploration, we will dissect the intricacies of electronics manufacturing services—examining the titans who shape the market, the value they add, and the challenges they face in a dynamic sector. Through this lens, we will scrutinize the processes that underpin EMS, the significance of supply chain management, the rigor of quality standards, and the burgeoning technologies setting the pace for future manufacturing marvels.
What is Electronics Manufacturing Services?
Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) refers to a comprehensive term used for companies that design, manufacture, test, distribute, and provide return/repair services for electronic components and assemblies for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). The concept is also referred to as electronics contract manufacturing (ECM). EMS providers are specialized entities that allow OEMs to focus on their core competencies like research and development of the products, while the EMS deal with the actual production.
Definition and Overview
Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) encompasses multiple facets of the electronics production cycle. This type of service can range from the design and prototype development of an electronic product, through the manufacturing and testing of electronic devices to logistics and post-manufacturing support. The EMS model has become integral to the business model of electronics companies that require the production of complex products with high-quality standards. EMS vendors employ advanced manufacturing technologies and are adept in dealing with the various electronics manufacturing challenges that can arise throughout the manufacturing process.
Not to be confused simply with the assembly of circuit boards, EMS stretches to cover comprehensive supply chain management services, guaranteeing OEMs a smooth transition from the product introduction phase all the way through to getting the product to market. Electronics Design Engineering services are also often part of the EMS offering, ensuring that the engineering aspects are tightly integrated into the overall manufacturing processes.
Importance in the Electronics Industry
The role of EMS providers is becoming increasingly important in the electronics manufacturing industry. They offer a partnership model that allows electronics manufacturers to scale efficiently without investing heavily in factories, machinery, or labor. By leveraging the decades of experience and established quality standards of EMS providers, OEMs can ensure that their electronic components and consumer electronics are built to the highest standards, while also being cost-effective.
EMS companies enable a quick turnaround for the production of electronic devices, which is crucial in a market where product types and consumer demands are constantly evolving. Additionally, with a focus on continuous innovation and adopting cutting-edge technologies, EMS providers help OEMs stay competitive in an industry that is marked by rapid changes. As the electronics manufacturing services market continues to grow, the reliance on these services by established and emerging electronics companies is a clear indication of their importance in manufacturing intricate and innovative products.
By handling everything from the assembly process to final quality assurance, EMS providers streamline the production process and ensure that the increasingly complex products reach the market in a timely manner, therefore playing a key role in the overall supply chain efficiency for consumer electronics goods.
History of Electronics Manufacturing Services
The Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) industry has a rich history that reflects the evolution of the global electronics sector. It is an industry born out of the need for electronics companies to optimize their operations by offloading the manufacturing aspects to more specialized firms. This shift allowed for a more focused approach to product development and innovation, while trusted partners took on the heavy lifting of mass-producing the items.
Early Developments in the Industry
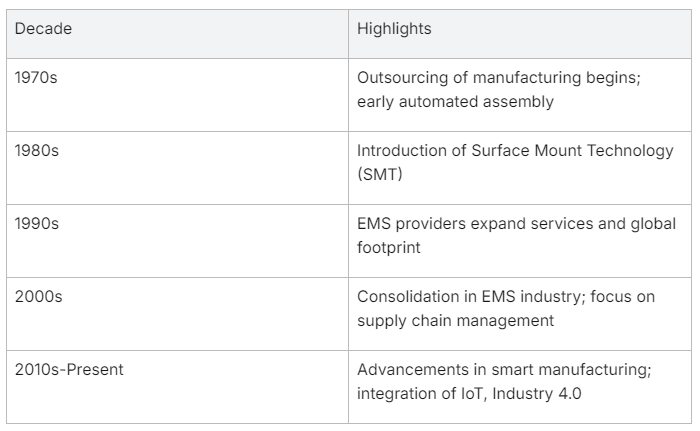
The inception of the EMS industry can be traced back to the 1970s. During this period, electronics started to infiltrate every aspect of daily life, leading to increased demand for electronic devices. While initially, most original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) maintained in-house production, the complexity and cost of manufacturing began to escalate. This era marked the start of outsourced manufacturing in more cost-effective locations and laid the foundation for contract-based production, which would eventually evolve into full-service EMS.
One of the early milestones for Electronics Manufacturing Services was the shift from manual assembly to automated processes. As the complexity of circuit boards grew, automation became essential—not only to increase productivity but also to maintain the quality standards required by advancing technologies. This automation eventually led to the development of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) in the 1980s, which significantly boosted efficiency in assembling electronic components onto circuit boards.
Growth and Evolution of EMS Companies
From the 1980s onwards, the EMS industry witnessed considerable growth and diversity. Companies that had started by offering basic assembly services expanded to offer comprehensive turnkey solutions, including design assistance, in-circuit testing, supply chain management, and even after-sales services. This comprehensive offering became a strong selling point for EMS providers, as it facilitated a faster time-to-market for OEMs’ products and allowed them to be more agile in response to changing market dynamics.
With increased globalization and the opening up of markets, EMS companies also began expanding their footprint worldwide. Asia, particularly China, emerged as a key hub for electronics manufacturing due to its cost advantage and manufacturing scale. EMS providers set up massive operations, developing entire campuses dedicated to the production of a wide array of electronic products.
A table illustrating the growth and evolution of EMS companies might include key milestones:
As technology continued to leap forward, the 2000s saw a consolidation in the EMS space, with larger players acquiring smaller or specialist firms, allowing them to tap into new markets and broaden their service portfolios. Towards the end of the 20th century and into the 21st, EMS companies have become integral to the electronics landscape, providing the backbone for the production of everything from consumer electronics to complex industrial systems.
EMS providers have now woven in advanced manufacturing technologies, such as robotics, AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT), to stay ahead of the electronics manufacturing challenges. This era of digital transformation—often referred to as Industry 4.0—has heralded new efficiency levels and customization capabilities, signaling a new phase in the growth and evolution of EMS companies.
Key Players in the Electronics Manufacturing Services Market
The Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) market is populated by a variety of players, ranging from large international conglomerates to specialized niche companies. These key players dominate the market by offering a suite of services that can cover the entire electronics product lifecycle, including design, engineering, manufacturing, assembly, testing, distribution, and after-sales support.
Overview of Major EMS Providers
When examining the roster of major EMS providers, a few names invariably come to the forefront. Companies such as Foxconn (Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd.), Pegatron Corp., Flex Ltd., Jabil Inc., and Wistron Corporation are often at the top of the list due to their extensive capabilities, vast infrastructure, and global reach. These EMS giants serve a diverse array of industries, ranging from consumer electronics to automotive and healthcare systems.
- Foxconn: Perhaps the most well-known, largely due to its association with Apple, Foxconn stands as the world’s largest electronics contract manufacturer in terms of revenue.
- Flex: This Singapore-based provider offers a comprehensive portfolio of services and maintains a strong presence across various industries and markets.
- Jabil: Headquartered in the United States, Jabil is recognized for its advanced manufacturing technologies and robust supply chain management solutions.
- Wistron: Known for computer manufacturing, Wistron has expanded its focus to include telecommunications and artificial intelligence products.
These companies, among others, are renowned for their decades of experience, which position them to tackle the complex challenges inherent in electronics manufacturing.
Market Share and Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the EMS market is both dynamic and demanding. Market share amongst the top players is continuously in flux as companies vie for larger contracts, engage in mergers and acquisitions, and extend their service offerings.
The EMS market also features several fast-growing small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that offer specialized services or focus on particular niches within electronics manufacturing. Such companies often bring innovative business models and flexibility to the table, which can be attractive to OEMs with specific needs or looking for more agility in the production process.
Overall, the EMS market is characterized by a concentration of large players with an expansive global presence while still maintaining room for smaller, innovative companies that offer tailored solutions. A successful EMS provider typically adopts a customer-centric approach, aligns with quality standards, utilizes the latest manufacturing technologies, and features a comprehensive supply chain management system. As OEMs continue to face complex and varied challenges, the demand for reliable and adaptable EMS partners remains strong.
Value Proposition of Electronics Manufacturing Services
The value proposition of Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) lies in their ability to enhance the competitive edge of original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). EMS providers integrate cutting-edge manufacturing processes and engineering services to deliver end-to-end solutions that span from concept design to end-of-life product management. By leveraging advanced manufacturing technologies and decades of experience, EMS companies offer a blend of quality, efficiency, and innovation that can be challenging to replicate in-house.
Advantages of Outsourcing to EMS Providers
Outsourcing to EMS providers grants several strategic advantages to OEMs. One significant benefit is cost reduction, as EMS companies typically have economies of scale and more competitive supply chain management. This cost efficiency allows OEMs to focus on their core competencies, such as R&D and marketing, while the EMS handles production. Additionally, outsourcing minimizes the need for OEMs to invest in their own manufacturing facilities and technology, which can be capital intensive.
Moreover, EMS providers have established expertise in navigating the complex regulatory and compliance landscape, a non-trivial aspect of electronics manufacturing that often requires a dedicated team and continuous monitoring. By tapping into EMS services, OEMs can ensure their products meet the necessary quality standards without the overhead of managing compliance themselves.
Here’s a simple table summarizing these advantages:
Benefits of Partnering with EMS Companies
Partnering with EMS companies extends an array of benefits that can propel an electronic product from inception to market dominance. Agility is one of the chief benefits; EMS companies can ramp up or down production based on market demands, providing OEMs with the flexibility to respond to industry trends quickly. This flexibility is vital for the successful introduction of innovative products in the highly competitive consumer electronics market.
Another benefit is the access to a vast network of electronic components and expertise in supply chain management. EMS providers manage global chains that can mitigate risks such as part shortages or logistical delays, which are common challenges in the electronics manufacturing industry. This capability ensures a steady flow of materials and components, which is crucial for timely product introduction and market delivery.
A partnership with an EMS provider often attracts comprehensive after-sales support services, which are pivotal for maintaining consumer satisfaction and brand reputation. These services, including repair, refurbishment, and warranty management, can be tailored to the OEM’s requirements, enhancing the overall value offering to their end-users.
Here’s a summarized list of the benefits:
- Agile response to market trends and demands
- Risk mitigation in supply chain disruptions
- Accelerated product introduction process
- Enhanced production capacity and scalability
- Advanced technological capabilities without significant investment
- Comprehensive after-sales support services
Electronics Manufacturing Services Process
The Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) Process encompasses a comprehensive range of activities that facilitate the creation of electronic devices and products. From the assembly of electronic components to the execution of detailed supply chain management, EMS encompasses all the services required to bring electronic products from idea to the consumer. With the relentless pursuit of efficiency and quality, EMS provides a collaborative business model that aligns with the operational needs of OEMs, ensuring innovative products reach the market both promptly and cost-effectively.
Steps Involved in EMS Process
The EMS process can be complex and multifaceted, involving several critical steps to ensure the successful production and delivery of electronic goods. Here is an encapsulated view:
- Design & Engineering: In this initial phase, the EMS provider collaborates with the OEM to conceptualize and elaborate the electronics design, paying heed to functionality, manufacturability, and regulatory compliance.
- Prototyping: Before mass production, prototypes are developed to test and validate the design. This step ensures that any potential issues are identified and corrected early in the manufacturing process.
- Component Sourcing: EMS providers manage the procurement of electronic components, leveraging their expansive supply networks to secure high-quality materials and mitigate risks like scarcity or obsolescence.
- PCB Assembly: The Circuit Board, which serves as the foundation of most electronic products, is assembled. This involves placing and soldering components onto the PCB following the design specifications.
- Product Assembly: After PCB assembly, the product undergoes further assembly processes, integrating various elements into the final product’s housing and ensuring it is functionally intact.
- Testing & Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing is conducted to ensure each product meets the established quality standards. This may include functionality tests, stress tests, and environmental simulations.
- Packaging & Logistics: Once the products are tested and Quality Assurance (QA) approved, they are packaged and prepared for distribution. EMS providers often manage logistics to ensure timely delivery.
- After-Sales Support: The EMS process also often includes after-sales services such as warranty processing, repairs, or product refurbishment to maintain high levels of customer satisfaction.
Overview of Manufacturing Technologies Used
EMS providers deploy a plethora of advanced manufacturing technologies to execute the aforementioned steps efficiently and effectively. Key technologies include:
- Automated Surface Mount Technology (SMT): Machines swiftly place components on PCBs, enhancing accuracy and speed.
- Selective Soldering: This process allows for precision in soldering components, beneficial for complex boards with dense component layouts.
- 3D Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): This technology inspects solder joints and verifies component placement, detecting potential assembly defects.
- X-Ray Inspection Systems: X-ray technology is used to inspect PCBs for quality assurance, particularly useful for identifying issues beneath components.
- Conformal Coating Machines: These machines apply a protective coating to PCBs, safeguarding electronic circuits against moisture, dust, and other environmental factors.
By utilizing these and other advanced technologies, EMS companies ensure the manufacturing process is efficient, reliable, and capable of producing high-quality electronics that meet today’s demanding market needs.
Challenges in Electronics Manufacturing Services
The world of electronics manufacturing services is one that is constantly evolving, driven by advances in technology and changes in consumer demands. However, with innovation and growth come significant challenges that manufacturers must navigate to stay competitive.
One major challenge is dealing with Supply Chain Risks. The global nature of electronics supply chains exposes manufacturers to a variety of risks, from geopolitical tensions to trade disputes. Volatile markets can also impact the cost and availability of raw materials and components, leading to production delays and increased prices.
Another pressing issue is Managing Quality Control and Compliance. As electronic devices become more complex, ensuring that each component meets the required quality standards can be a daunting task. Compliance with international standards and regulations adds another layer of complexity, making it critical for manufacturers to have rigorous quality control processes in place.
Both of these challenges require strategic planning, robust systems, and sometimes, a bit of agility to overcome, ensuring that electronics manufacturing services can continue to thrive in the current industrial landscape.
Addressing Supply Chain Risks
In the realm of electronics manufacturing services, supply chain risks can have a significant impact on production timelines and overall product quality. Manufacturers must adopt strategies to address these risks to maintain a reliable supply chain. Some effective approaches include:
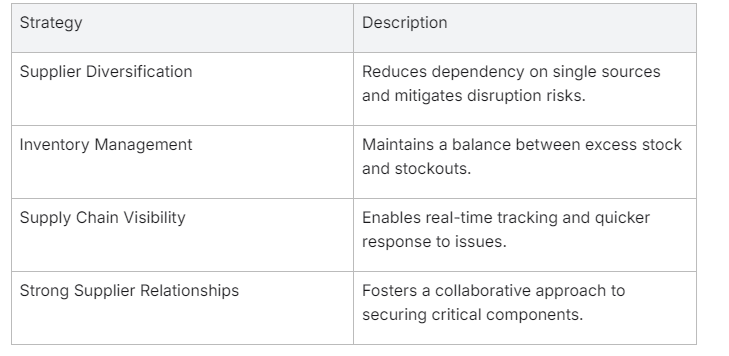
- Diversifying Supplier Base: By not relying on a single source for components, manufacturers can mitigate the risk of supply chain disruptions.
- Flexible Inventory Management: Keeping a buffer stock or exploring just-in-time inventory strategies can help manage fluctuations in demand and supply.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Implementing advanced tracking and monitoring systems ensure transparency across the supply chain, allowing for proactive risk management.
- Building Strong Relationships with Suppliers: Collaborative relationships lead to better communication and often, preferential treatment during shortages.
A table summarizing key strategies for supply chain risk management:
Managing Quality Control and Compliance
Quality control and compliance are non-negotiable aspects of electronics manufacturing services. To maintain high quality and meet compliance standards, manufacturers must implement robust processes and often, make significant investments in both resources and technologies.
Ways to manage these aspects include:
- Implementing International Standards: Adhering to standards like ISO 9001 can help establish a quality management system that is recognized globally.
- Regular Auditing and Testing: Internal and external audits coupled with rigorous product testing ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Training: Training employees on the latest quality control techniques and compliance requirements keeps production lines running effectively.
- Quality Assurance Technology: Advanced technologies such as 3D AOI and X-ray inspection systems are critical for maintaining product quality.
A list of critical technologies for managing quality and compliance:
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
- X-Ray Inspection Systems
- In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
- Functional Testing
- Environmental Testing Chambers
By proactively managing these challenges, electronic manufacturing services can not only improve their resilience and reliability but also strengthen their competitive edge in the market.
Trends and Innovations in Electronics Manufacturing Services
The landscape of electronics manufacturing services (EMS) is in a constant state of flux, with new trends and innovations continually shaping the way manufacturers operate. The industry has seen a pronounced shift towards more complex products incorporating advanced manufacturing technologies to improve efficiency and performance. A notable trend is the miniaturization of electronic components, which requires precision and expertise to produce smaller yet more powerful consumer electronics. There is also a growing emphasis on sustainability, with manufacturers incorporating eco-friendly materials and processes to meet consumer and regulatory demands.
The electronics manufacturing services market is increasingly embracing customization, enabling a more personalized consumer experience. This shift necessitates flexible manufacturing processes and innovative product introduction strategies to facilitate product to market at a faster pace. The use of data analytics to refine manufacturing processes and predictive maintenance to minimize downtime are also trending, showcasing the industry’s turn towards smart manufacturing practices.
In the following sections, we will delve into the specifics of how EMS providers are adopting advanced manufacturing technologies and embracing Industry 4.0 to stay at the forefront of innovation.
Adoption of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
In an industry driven by the constant demand for smaller, faster, and more reliable electronic products, the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies in EMS is essential. One of the primary technologies being integrated is 3D printing, otherwise known as additive manufacturing, which allows for rapid prototyping, custom components, and complex geometries that are impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing.
Automation and robotics are being increasingly used in assembly lines to boost throughput and improve the accuracy and repeatability of the assembly process. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are finding their place in optimizing every step of the manufacturing process, from supply chain logistics to final quality control inspections. These tools can predict machine failures, optimize production schedules, and even improve the efficiency of the electronics design and engineering services.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another technology that is becoming prevalent in EMS. With connected sensors and devices, manufacturers can gain real-time insights into the production process, allowing for improved supply chain management and efficiency. IoT platforms are enabling smart inventory management, which anticipates the need for components before they run out, thus preventing potential bottlenecks.
Embracing Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Industry 4.0, characterized by the digitization of manufacturing processes, is revolutionizing the electronics manufacturing services industry. Embracing Industry 4.0 means integrating digital technologies like the IoT, AI, big data analytics, and cyber-physical systems to create a ‘smart factory’ environment. This transition aids EMS providers in achieving higher levels of customization and flexibility in their production processes.
The use of real-time data analytics not only optimizes the manufacturing process but also enhances the decision-making capabilities of management, providing more insights into the electronics manufacturing challenges and enabling quicker product introduction.
Moreover, digital twins—virtual replicas of physical devices—allow for the simulation and analysis of production systems before they are built, which can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with bringing a new electronic product to market.
In smart factories, collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside humans, improving safety and efficiency. The agility of a smart manufacturing setup also meets the demands of producing complex products in a cost-effective manner, allowing for more versatile business models within the electronics manufacturing sector.
Embracing Industry 4.0 technologies provides EMS providers with a competitive edge by offering enhanced supply chain management, advanced manufacturing technologies, and improved quality standards. This comprehensive integration of innovative approaches paves the way for a more robust, agile, and customer-focused electronics manufacturing landscape.
Importance of Supply Chain Management in EMS
In the fast-paced realm of Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS), Supply Chain Management (SCM) emerges as a critical factor that goes beyond mere coordination of materials and components. Effective SCM holds the key to ensuring that electronic products are delivered on time while maintaining high-quality standards and cost-competitiveness. With numerous elements such as raw materials, electronic components, and logistics playing integral roles, the importance of a well-orchestrated supply chain cannot be understated.
A robust supply chain management system can make all the difference in an industry where time-to-market and agility are crucial. It enables EMS providers to respond swiftly to changes in consumer demand, mitigate risks associated with procurement and disruptions, and maintain a seamless flow from component sourcing to final product delivery. Furthermore, it can lead to increased operational efficiency, reduced excess inventory, and better management of the entire product lifecycle, ultimately resulting in a stronger bottom line for businesses.
Overview of Supply Chain Management in Electronics Manufacturing
Each link in this supply chain is essential, with inventory levels, demand forecasting, and supplier performance dictating the rhythm of the entire production process. Costs, quality control, and the speed of production hinge on an optimally managed supply chain, making it a cornerstone of successful electronics manufacturing operations.
Strategies for Streamlining the Supply Chain
Streamlining the supply chain involves a range of strategies aimed at optimizing efficiency and reducing waste:
- Lean Inventory Management: Adopt a “just-in-time” approach to minimize excess inventory without risking shortages, which can be achieved through refined forecasting tools and demand planning.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Forge strong relationships with suppliers and establish performance metrics to ensure reliability and high quality of electronic components.
- Advanced Planning Systems: Leverage advanced planning and scheduling (APS) software to improve the accuracy of production schedules and integrate them with supply and demand planning.
- Automation and Technology: Implement automation tools for routine processes, as well as data analytics, to track the performance and anticipate disruptions in the supply chain.
- Logistics Optimization: Optimize logistics and distribution strategies, including multi-modal transportation solutions, to ensure cost-effective and timely delivery.
Integrating these strategies can lead to a more resilient and responsive supply chain, capable of adapting to industry demands and fluctuations, thus providing enhanced service to customers and a competitive advantage in the market.
Engineering Services in Electronics Manufacturing
In the sophisticated arena of Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS), engineering services are a vital cog in the machine that drives innovation and efficiency. These services often encompass a wide range of technical and logistical support activities, all designed to refine the end product and enhance the manufacturing process. This includes research and development (R&D), prototyping, design analysis, and testing of electronic devices or components.
By employing a critical eye and decades of experience, electronics manufacturers deploy these services to solve complex product challenges. They use advanced manufacturing technologies to deliver devices that meet strict quality standards, thus ensuring they hold their own in the dynamic consumer electronics market. These engineering services form the backbone of any EMS provider looking to build a reputation for excellence and reliability.
Role of Engineering Services in EMS
Engineering services play a multifaceted role in the world of EMS, melding seamlessly into multiple stages of the development and manufacturing cycle. At the inception of a project, engineering services are pivotal for the electronics design process. These services guide the translation of a concept into a viable electronic product, taking feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and potential market impact into consideration.
- Product Engineering: This involves refining the product design to enhance functionality and optimize manufacturability.
- Process Engineering: It’s about devising efficient manufacturing processes and assembly lines.
- Test Engineering: Developing sophisticated testing procedures to ensure the product meets rigorous standards before it enters the market.
These services ultimately result in reducing the manufacturing partner’s risk and aiding in a smooth product introduction. Integrated with the assembly process, engineering services also assist in pinpointing and rectifying production bottlenecks, contributing to better overall performance of the electronics manufacturer.
Importance of Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
A fundamental aspect of engineering services, Design for Manufacturing (DFM) stands out for its ability to marry design and production in the quest for operational perfection. DFM’s primary goal is to simplify and perfect the complexities of the manufacturing processes by aligning the design of electronic devices with the capabilities of the manufacturing system.
- Cost Reduction: DFM scrutinizes every product design aspect to cut unnecessary costs without compromising quality.
- Enhanced Product Quality: By considering manufacturing constraints in design, DFM leads to higher-quality products that meet consumer expectations.
- Efficiency: DFM-optimized designs minimize the number of parts and simplify assembly steps, leading to faster production times.
This approach not only streamlines the creation of complex products but also accelerates the time it takes to transition from product to market.
By incorporating DFM principles, electronics manufacturing services can ensure their business model thrives on innovation while staying grounded in practical, cost-effective manufacturing solutions. As product types evolve and the demands of the electronics manufacturing industry shift, DFM remains an indispensable strategy in the pursuit of excellence.
Quality Standards in Electronics Manufacturing Services
In the highly competitive world of electronics manufacturing services (EMS), adhering to stringent quality standards is not just beneficial; it’s a baseline expectation. Clients and end-users demand that electronic products operate reliably under various conditions and over extended periods. Electronics manufacturers, therefore, integrate quality assurance into every stage of their manufacturing process to ensure that the final products are of the highest possible standard.
Quality in EMS is multidimensional, encompassing everything from the robustness of the electronic components used to the precision of the assembly process. Standards are set and measured in terms of product performance, durability, and compliance with both industry-specific and international regulations. High-quality standards can lead to improved product longevity, increased safety, enhanced performance, and overall customer satisfaction.
Moreover, quality standards are not static. They evolve to keep pace with new technologies, manufacturing processes, and market trends. Electronics manufacturers must stay abreast of these changes to maintain their competitive edge and ensure their products meet or exceed the prevailing standards.
In summary, electronics manufacturing services prioritize quality standards to not only fulfill customer expectations but also to align with legal and industry requirements, thereby reinforcing their position in the market as reliable manufacturers of electronic products.
Overview of Quality Certification Programs
Quality certification programs serve as verifiable indicators that an electronics manufacturer has met strict standards in their production processes and end products. These programs are often developed by international or industry-specific organizations and require rigorous audits and continuous compliance to maintain certification. Among the most recognized quality certification programs in the electronics manufacturing industry are:
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO):
- ISO 9001: The most widely adopted standard for quality management systems, ensuring that companies consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- ISO 14001: Focuses on effective environmental management systems to enhance environmental performance.
- ISO/IEC 27001: Pertains to information security management systems, crucial for the protection of sensitive electronic data.
- IPC Association Connecting Electronics Industries: Offers multiple certification programs, including:
- IPC-A-610: The Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies, which is the most widely used electronics assembly standard in the world.
- Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG):
- IATF 16949: Specific to the automotive sector, this standard is based on ISO 9001 with additional requirements for the automotive industry.
- Aerospace Quality Group:
- AS9100: Based on ISO 9001 with additions and interpretations specific to the aerospace industry, including requirements that are crucial for flight safety and quality.
These certifications are not mere badges of honor; they provide a framework for continuous improvement, risk management, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Electronics manufacturing services companies often use these certifications to demonstrate their commitment to quality and to differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace.