This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
FPGA Power-On-Reset Design and Implementation
08/06/2019, hardwarebee
Power-On Reset is an electronic circuit that generates a reset pulse, which sets the entire design to an initial and well-known state after the power supply is detected. In Vivado the Xilinx’s Processor System Reset LogiCORE IP provides this functionality.
If a synchronous reset is executed at system startup, it is possible that there is no clock signal at this time, since the clock source itself may be subject to a reset. Therefore, the synchronous reset can be ineffective.
Often the Power-On Reset (POR) is generated by an external device, for example the watchdog, which monitors the supply voltage or the activity of a microprocessor. Then the POR is also not synchronous to the system clock.
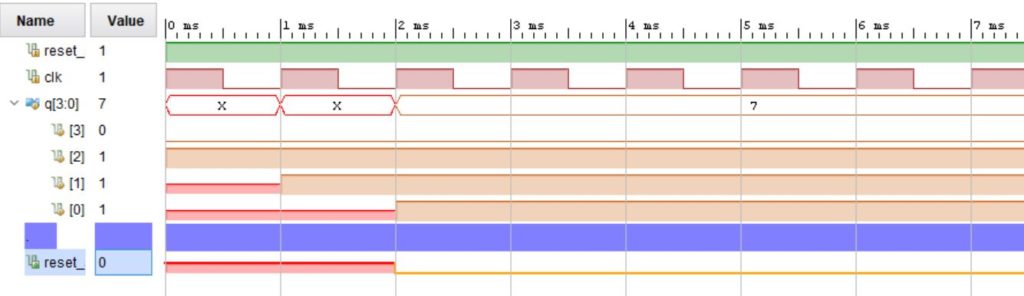
The following circuit generates a reset signal from the external POR (in this example low active) which becomes active high for at least 3 clock cycles and then becomes inactive synchronously with the clock. It is crucial that the reset signal is not deactivated within the setup time of a memory, ie shortly before a clock edge!!!
The external POR signal sets the 3 flip-flops of the shift register asynchronous to ‘0’ (= reset). Since it is asynchronous to the system clock, it is called reset_a and is active low.
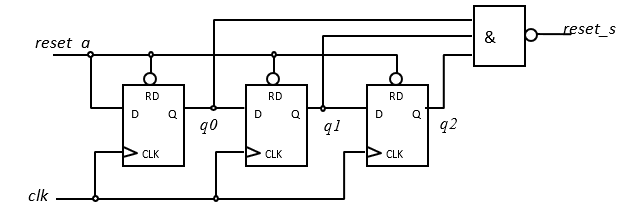
After the POR signal has been deactivated, its inactive value ‘1’ is clocked into the shift register as soon as the system clock is present. The first two flip-flops prevent a possible metastable state from affecting the synchronized reset_s signal, otherwise the entire system would be put into an undefined metastable state. After 3 clocks all outputs of the 3 flip flops are set to the value ‘1’, which means that the triple NAND gate changes from the value ‘1’ (active reset_s level) to the value ‘0’ (inactive reset_s level ) changes.
Code implementation in HDL
With FlipFlops in series:
Verilog
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module aufgabe2_1(
input reset_a,
input clk,
output reset_s
);
reg q0,q1,q2;
//Always beschreibt die 3 FlipFlop Speicherelemente
always@(posedge clk, reset_a)
begin
if (reset_a == 1‘b0) //reset_a ist asynchron zu clk
begin
q0 <= 1′b0;
q1 <= 1‘b0;
q2 <= 1′b0;
end
else if (clk == 1‘b1)
begin
q0 <= reset_a;
q1 <= q0;
q2 <= q1;
end
end
//nebenläufige kombinatorische Logik
assign reset_s = !(q0 & q1 & q2);
endmodule
|
VHDL
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
LIBRARY ieee;
USE ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
entity por is
port(
reset_a: in std_logic;
clk: in std_logic;
reset_s: out std_logic
);
end entity por;
—
architecture rtl of por is
signal q0,q1,q2: std_logic;
begin
—process beschreibt die 3 FlipFlop Speicherelemente———–
process(clk,reset_a)
begin
if reset_a = ‘0’ then — reset_a ist asynchron zu clk
q0 <= ‘0’;
q1 <= ‘0’;
q2 <= ‘0’;
elsif clk=’1’ and clk’event then
q0 <= reset_a;
q1 <= q0;
q2 <= q1;
end if;
end process;
—nebenläufige kombinatorische Logik——
reset_s <= not (q0 and q1 and q2);
end architecture rtl;
|
The waveform after the simulation looks like:
Using a shift register
Verilog
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module aufgabe2_1b(
input reset_a,
input clk,
output reset_s
);
reg [3:0] q;
always@(posedge clk,reset_a) //auch reset_a muss in der Sensitivity–Liste stehen!!!
begin
//process beschreibt die 3 FlipFlop Speicherelemente
begin
if(reset_a == 1‘b0) //reset_a ist asynchron zu clk
q <= 3′b000; //alle Elemente des Vektors q auf ‘0’ setzen
else if( clk == 1‘b1)
q <= {reset_a , q[2:1]}; //Schieberegister, rechts schiebend
end
end
//nebenläufige kombinatorische Logik
assign reset_s = (q == 3′b111) ? 1‘b0 : 1’b1;
endmodule
|
VHDL
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
LIBRARY ieee;
USE ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
entity por is
port(
reset_a: in std_logic;
clk:in std_logic;
reset_s: out std_logic
);
end entity por;
—
architecture rtl of por is
signal q: std_logic_vector(2 downto 0);
begin
—process beschreibt die 3 FlipFlop Speicherelemente———–
process(clk,reset_a) –– auch reset_a muss in der Sensitivity–Liste stehen!!!
begin
if reset_a = ‘0’ then— reset_a ist asynchron zu clk
q <= (others => ‘0’); — alle Elemente des Vektors q auf ‘0’ setzen
elsif clk=’1’ and clk’event then
q<= reset_a & q(2 downto 1); —Schieberegister, rechts schiebend
end if;
end process;
—nebenläufige kombinatorische Logik——
reset_s <= ‘0’ when q = “111” else ‘1’;
end architecture rtl;
|
______________________________________________________________
This is a guest post by Alberto Lopez which was originally published on Mis Circuitos