This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Y Capacitor
16/12/2021, hardwarebee
When electronic equipment is linked to the AC mains, common-mode electrical noise can be generated. If this is permitted to return to the mains supply line, it may cause problems for other equipment connected to the same line. Y capacitors are used to filter the common-mode noise out.
Manufacturers include capacitor-based power line filtering into their systems to isolate any common-mode noise generated by the device’s power source from reaching other equipment through the mains power line. The safety of the equipment’s users is dependent on the capacitors’ dependability.
X-capacitors and Y-capacitors are the two types of line filter capacitors. To defend against differential mode interference, X-capacitors are linked between the line and the neutral. Their failure does not result in a deadly electric shock, but it does pose a fire hazard. Y-capacitors, on the other hand, are meant to filter out common-mode noise and are linked between the line and the chassis; if they short-circuit, the user risks being shocked.
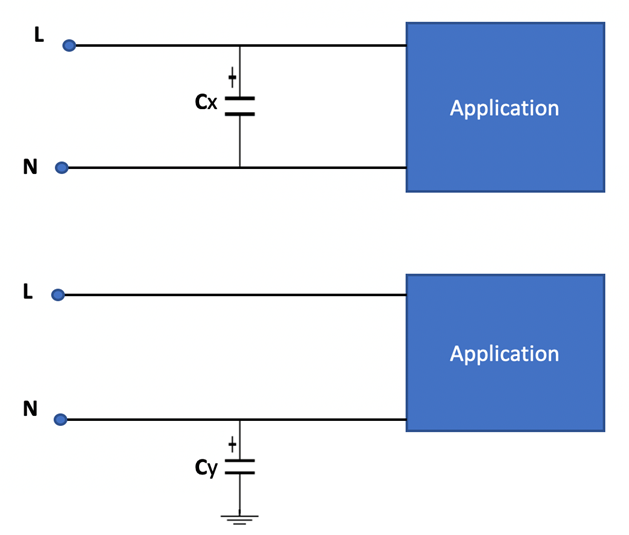
Figure 1: Placement of Class-X (CX) and Class-Y (CY) safety capacitors.
Capacitor types used in line filters
Metalized paper/film and ceramic are two common types of capacitors. Ceramic versions of Y-capacitors are less costly than metallized film, however they are less mechanically stable and unstable with time and temperature. Ceramic failure modes are also more likely to be short circuited, whereas metallized paper and film failure modes are more likely to be open circuited.
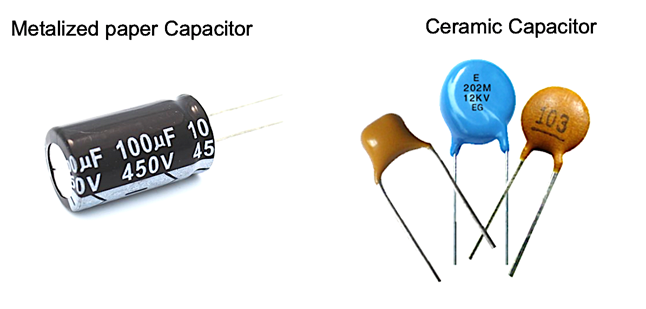
Figure 2: Common types of Capacitors
Y-capacitor sub-classifications
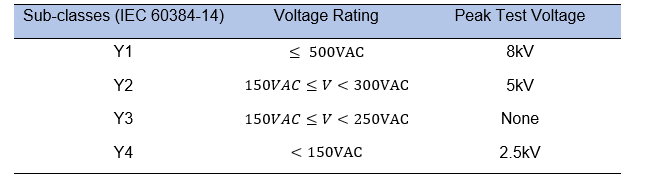
Class-Y capacitors are classified based on their peak voltage/rated voltage, as well as the peak impulse voltage that they can safely tolerate. Y-capacitors have sub-classifications defined by IEC 60384-14. Y-capacitors are classed as Y1, Y2, Y3, or Y4 depending on the kind of bridging insulation and the AC and peak voltage ratings. Capacitors of the Y1 class are rated up to 500VAC and have an 8kV peak test voltage. Y2 capacitors have a voltage rating of 150 to 300 VAC and a peak test voltage of 5kV. The peak test voltage for Y3 capacitors is not defined, however it is rated at 250VAC. The Y4 capacitors have a 150VAC rating and a peak test voltage of 2.5kV. Table 1 summarizes the subclasses of Class-Y capacitors.
Table 1. Class-Y subclass ratings*
* According to Kemet, the following international standards apply:
- UL 1414: UL 1414 is an American standard for cross-line applications.
- UL 1283: Standard for electromagnetic interference filters in the United States.
- CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 1: applications across the line
- CAN/CSA 384-14: applications across the line
European standards for Y-capacitors
Y-capacitors are built to meet stringent electrical and mechanical reliability requirements. When AC voltage is supplied, capacitor values are regulated to lower the current going through the capacitor, and when DC voltage is applied, capacitor values are limited to keep the energy stored to a safe level. To be used as Y-capacitors, capacitors must be tested to suitable standards.
The EN 132400 Standard was published on June 26, 1995, and it superseded all previous European National Standards. This was the same as the IEC 60384-14 2nd Edition 1993 International Standard. Since then, the European Standard EN 132400 has been superseded by EN 60384-14, which is similar to the International Standard IEC 60384-14, in order to keep CENELEC and IEC standards identical in name and specification. Any European national authority can grant approvals, and the validity of such approvals is accepted by all other CENELEC member nations’ authorities, eliminating the need to redo the tests.
Other areas’ applicable standards are: UL 1414 for cross-connection applications and UL 1283 for Electromagnetic Interference filters in the United States. CAN/CSA C22.2N°1 and CAN/CSA 384-14 in Canada. GB/T14472 China.
IEC/EN 60384-14 includes critical tests such as impulse voltage, durability, and active flammability. The capacitor classification and sub-classification determine the application and conditions for these tests.
Applications for Class-Y Capacitors
The most often used safety-certified capacitors are of subclass Y2. They’re generally the ones you’ll want to utilize, depending on your application and requirements. This is based on the fact that Y2 safety capacitors are utilized in everyday products that plug into standard household wall outlets. To be clear, you should choose your Class-Y capacitors based on the purpose and needs of your design, with Y2 capacitors suitable for residential applications and Y1 safety capacitors suitable for industrial applications. You could, of course, employ subclass Y1 in non-industrial applications, but you’ll pay more and the bigger sizes may be uncomfortable.
An X2 capacitor can be safely substituted for a Y2 capacitor, however a Y2 capacitor should not be substituted for an X2 capacitor. This is due to the fact that, while an X2-type capacitor would function and filter noise adequately, it would not fulfill the line-to-ground safety criteria. Safety capacitors of the Y2 series are more durable, can handle greater peak impulse voltages, and are designed to fail open rather than short.
There are also safety capacitors that combine the best features of class X and Y kinds, ensuring that they meet both X and Y safety criteria. In a line-to-line application, an X1/Y1 combination simply implies that the capacitor may be utilized as an X1 capacitor or as a Y1 capacitor.










