FPGA Video Processing: Ultimate Guide
27/03/2025, hardwarebee
Imagine watching high-resolution video streaming seamlessly without a hitch; the magic behind such captivating visuals often lies within a tiny piece of technology known as the FPGA. Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) have revolutionized video processing by introducing unparalleled flexibility and dynamic performance capabilities, making them a staple in innovative video solutions. These versatile devices are not merely components; they are transformative tools in the realm of digital video technology.

In the world of video processing, understanding the intricate components like video and image processing suites, gamma correctors, alpha blending mixers, and more require keen expertise. FPGAs play a crucial role in driving applications such as 4K Ultra HD video processing, bridging, and aggregation techniques. Whether it’s leveraging the benefits like customizability and efficiency or mastering system design through camera interfaces and VGA drivers, the depth of FPGA’s impact is profound.
This comprehensive guide delves into the vast landscape of FPGA video processing, offering insights into optimal performance techniques like kernel implementations and threshold adjustments. Through engaging case studies and detailed tutorials, both beginners and seasoned professionals can gain invaluable knowledge. Join us as we explore expert insights and best practices that highlight the sophisticated yet accessible world of FPGAs in video technology.
Understanding Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
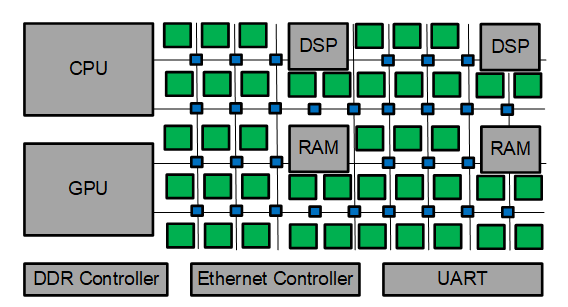
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are versatile integrated circuits used in various tech applications, especially video processing. They are reprogrammable, meaning their logic gates can be configured for specific tasks even after manufacturing. This makes them ideal for real-time image processing and video feed applications.
FPGAs are central to video processing systems. They handle tasks such as color space conversion, chroma resampling, and frame buffering, all critical in a video processing pipeline. These tasks are executed with extreme hardware acceleration, benefiting from the FPGA’s capability for massive parallelism.
A typical video processing project with FPGAs involves several stages, like the integration of an image sensor, real-time processing using custom algorithms, and generating an output image. The Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGA, for example, is popular in these designs due to its robust performance.
Key Features of FPGAs in Video Processing:
- Reprogrammability: Customize for various applications.
- Real-Time Processing: Handle video feeds with minimal latency.
- Massive Parallelism: Execute many operations simultaneously.
- Hardware Acceleration: Deliver improved processing speed.
In summary, FPGAs are essential in video processing tasks, enabling efficient image processing designs and innovation in vision applications.
Components of Video Processing Systems
Video processing systems are complex networks that manage video and image data. They play a key role in converting raw footage into a format suitable for displays or further processing stages. Central to this system are components like frame buffers, which temporarily store video frames, and logic gates, which handle the data processing. These systems also use pipelines to guide video data through its various stages. The quality and efficiency of the output image depend on the system’s components working seamlessly together through these stages.
Video and Image Processing Suites
Video and image processing suites are collections of tools and applications that manage and refine video data. They often include functions like real-time image processing, color space conversion, and auto white balance. These suites are essential for handling tasks from image capture to final output. Blackmagic Design is one well-known provider, known for its robust systems. These suites also support machine learning applications, which can improve processing through intelligent algorithms. By integrating multiple processes in one package, they simplify complex workflows.
Gamma Correctors
Gamma correctors are vital in adjusting the brightness and contrast of an image or video. They modify the gamma levels, ensuring that what appears on screen matches the intended luminosity. This correction is crucial for maintaining color accuracy in vision applications and video channels. Gamma correction can be handled in real time, ensuring that every video frame displays consistently. With proper gamma adjustment, video feeds and output images maintain their quality regardless of the display device used.
Alpha Blending Mixers
Alpha blending mixers are used to combine multiple video layers or images into a single frame. They modify the transparency levels of overlapping images, allowing for smooth transitions and complex visual effects. This process involves the use of MIPI CSI-2 interfaces to stream data efficiently. In video processing systems, these mixers are crucial for creating cohesive images from different sources. By managing transparency and blending, they contribute to producing intricate and visually appealing video content.
Applications of FPGAs in Video Processing
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are vital tools in video processing applications. An FPGA can be programmed to handle complex tasks in real time. This capability makes FPGAs ideal for video processing systems where speed and precision are critical. FPGAs are used in video processing pipelines to convert color spaces, resample chroma, and perform real-time image processing. They handle multiple video channels and video frames efficiently. These functions benefit vision applications like automated quality inspection and real-time surveillance. FPGAs support image processing algorithms, enabling them to make fast decisions based on input from cameras or image sensors.
4K Ultra HD Video Processing
Processing 4K Ultra HD video requires extreme hardware acceleration, and FPGAs are well-suited for this task. The Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGA, for example, offers high performance in processing high-resolution video. It can manage massive parallelism, allowing multiple processes to run simultaneously. This feature boosts the FPGA’s capacity to handle real-time video processing without bottlenecking the data flow. FPGAs convert incoming video feeds through color space conversion, preserving detail and color accuracy. They also use block diagrams in design, simplifying complex tasks like motion adaptive frame processing.
Bridging and Aggregation Techniques
FPGAs use bridging and aggregation techniques to enhance video processing capabilities. Bridging connects various components in a video processing system, ensuring data flows smoothly through the pipeline. FPGAs can aggregate data from multiple video channels efficiently, handling input from various cameras or sensors. These components communicate using standards like MIPI CSI-2, ensuring compatibility with different image processing designs. In this setup, frame buffers play a critical role. They store video frames, aiding in real-time image processing by offering quick access to needed data. This processed video provides precise output images, essential for machine learning and vision applications. Additionally, FPGAs include intellectual properties that support unique processing tasks. By leveraging these techniques, FPGAs ensure that video processing projects achieve high performance while maintaining system reliability.
Advantages of Using FPGAs in Video Solutions
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) offer significant advantages in video solutions. These chips are ideal for Real-Time Video Processing due to their speed and flexibility. Unlike traditional CPUs, FPGAs use extreme hardware acceleration to handle complex tasks simultaneously. This enables them to support high-resolution video feeds without delays. The parallel processing capability of FPGAs is beneficial for demanding video processing pipelines. They allow for seamless color space conversion and motion adaptive imaging. This makes FPGAs suitable for various vision applications, including machine learning and real-time image processing.
Flexibility and Customizability
FPGAs shine with their flexibility and customizability in video processing. Users can configure these chips to execute specific Image Processing algorithms. This allows developers to tailor solutions to meet exact project needs. The programmable nature of FPGAs makes them perfect for both simple and complex image processing designs, adapting to any task at hand. This customization extends to intellectual properties, enabling integration with various video channel interfaces. For instance, users can implement chroma resamplers or auto white adjustments per project specifics. Additionally, FPGAs facilitate smooth data flow through video frames with MIPI CSI-2 or Blackmagic Design protocols. This adaptability ensures video processing systems remain efficient and relevant, regardless of changing technology or project requirements.
Efficiency and Performance Optimization
Efficiency and performance are key when using FPGAs for video processing. These chips optimize tasks with massive parallelism, improving real-time image processing. FPGAs handle large data volumes swiftly, making them integral to any video processing pipeline. Their logic gates allow for high-speed processing while maintaining low power consumption. This results in output images that are both fast and energy-efficient. Moreover, FPGAs utilize frame buffers and motion adaptive logic to enhance video smoothness. The Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGA, for example, is renowned for such capabilities. These features enable it to support demanding video feeds efficiently. With the added ability to adjust for performance needs, FPGAs remain a preferred choice in building high-performing image processing systems.
System Design with FPGAs
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are powerful tools for building custom video processing systems. They offer extreme hardware acceleration through parallel processing, making it possible to handle real-time video feeds. In video processing projects, speed and flexibility are key. FPGAs provide the necessary environment to design systems using logic gates that can process video channels efficiently. The design phase involves creating block diagrams which map out the video processing pipeline, from the image sensor input to the output image. Real-time image processing often requires features like motion adaptive techniques and machine learning integration. By capitalizing on these capabilities, system designers can create advanced image processing systems tailored for specific vision applications.
Camera Interfaces and Connectivity
Connecting cameras to FPGAs is a crucial part of system design. FPGAs often use interfaces like MIPI CSI-2 to link with image sensors. MIPI CSI-2 is a standard protocol that efficiently transfers video frame data to the FPGA. This connectivity is essential for processing high-resolution video at high speeds. One important aspect of this setup is managing the data from multiple sources, which can involve using frame buffers to handle the video feed. By doing so, FPGAs can manage inputs from several video channels simultaneously. This is vital for complex applications like real-time video processing, where the speed of data transfer affects the system’s performance. Understanding and selecting the right interfaces ensures that video processing systems are efficient and reliable.
Implementing VGA Drivers
Implementing VGA drivers on FPGAs involves designing a versatile and efficient system to output images. The VGA driver converts processed video data into a format suitable for display monitors. This requires an understanding of color space conversion, which adjusts the colors to match display standards. The design of the driver includes a block diagram outlining the data flow from input to output. Designers must consider aspects like chroma resampling to maintain color fidelity and adaptively manage video frames. These components ensure smooth and accurate video playback on monitors. Additionally, the use of intellectual properties from companies like Xilinx, such as those in the Spartan-6 FPGA, facilitates the integration of advanced Video Graphics Array (VGA) functions. This allows for rapid deployment of VGA drivers, critical in displaying real-time video processing results effectively.
Techniques for Optimal FPGA Performance
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are a popular choice for video processing applications. They offer significant advantages in speed and flexibility compared to traditional processors. Achieving optimal performance with an FPGA involves more than just programming; it requires careful design and implementation of video pipelines. By leveraging innovations like massive parallelism and real-time image processing, you can process video feeds more efficiently. Utilizing intellectual properties (IPs) and block diagrams can also speed up development and enhance performance. Whether you are working on video processing projects that involve color space conversion or using logic gates for extreme hardware acceleration, optimizing the design of your video frame and video channel is essential.
Kernel Implementation
Implementing kernels on an FPGA can significantly enhance data processing speeds. The kernel serves as the core processing unit, performing operations such as filtering and transformation on video frames. By designing an efficient kernel, you can achieve real-time video processing with minimal delay. A well-implemented kernel can effectively handle image sensor inputs using AXI Stream protocols, ensuring smooth data flow. Optimizing kernel pipelines for specific tasks, like auto white balance or chroma resampling, further increases performance. Blackmagic Design and MIPI CSI-2 protocols enhance kernel data management, facilitating efficient video processing in vision applications.
Threshold Adjustment Strategies
Threshold adjustment is crucial for ensuring stable and precise video processing on FPGAs. This involves setting limits that dictate how image processing systems react to various inputs. Real-time adjustments can maximize processing accuracy, particularly in complex tasks like machine learning and motion adaptive processing. You can use techniques such as feedback loops to refine these thresholds efficiently. By adjusting thresholds dynamically, the output image quality improves, making the system more adaptive to real-world conditions. Developing strategies for threshold settings ensures that video feeds maintain clarity and responsiveness, crucial for real-time applications.
Case Studies on FPGA Video Processing
FPGA video processing offers significant opportunities in real-time video applications. It leverages extreme hardware acceleration and massive parallelism, transforming how video data is handled and interpreted. As more industries harness this technology, several innovative projects have emerged. These case studies reveal how different companies have implemented FPGA to solve complex video processing challenges. They highlight the potential of FPGA in improving system performance, reducing latency, and enhancing video quality across various applications. From 4K video conferencing to advanced imaging systems, these examples demonstrate the versatility and power of FPGA video processing solutions.
Aldec’s 4K Video Conferencing Solution
Aldec has developed a robust 4K video conferencing solution using FPGA technology. This application combines color space conversion and real-time image processing to deliver high-quality video feed. The solution is designed to handle large amounts of data effectively, ensuring seamless video communication. By utilizing the Xilinx Spartan-6 FPGA, Aldec’s system provides efficient image processing design and real-time output image. The use of frame buffers and chroma resampler ensures video frame accuracy and clarity. This solution showcases how FPGA can drive video processing systems to achieve high-performance video conferencing with low latency and high resolution.
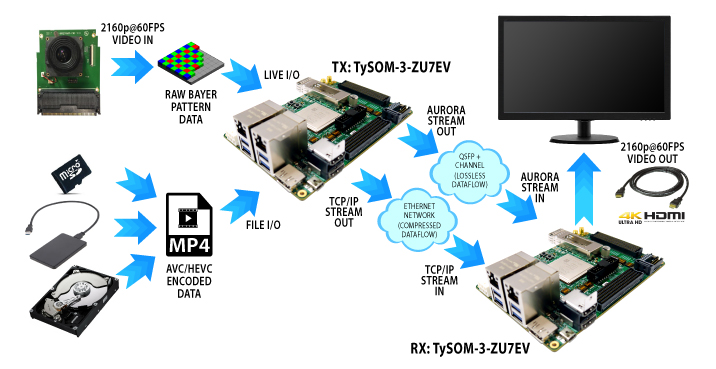
Insights from e-con Systems
e-con Systems is a leader in providing advanced vision applications using FPGA technology. Their approach harnesses the capabilities of FPGA to enhance video processing projects and image sensor technology. They use logic gates and intellectual properties to optimize image processing systems, resulting in improved video channel management and motion adaptive algorithms. By incorporating MIPI CSI-2 and AXI Stream interfaces, e-con Systems ensures high-speed data transmission across video processing pipelines. The company’s work exemplifies the integration of machine learning with FPGA, paving the way for real-time image processing and auto white balancing in challenging environments. This highlights the transformative impact of FPGA on modern video solutions.
Expert Insights and Best Practices for FPGA Video Processing
FPGA video processing is an exciting field with many applications. Experts suggest focusing on several key areas to optimize performance. Here are some best practices:
- Real-Time Processing: Use FPGAs for real-time video processing to manage video feeds more efficiently. FPGAs like the Xilinx Spartan-6 excel at extreme hardware acceleration, allowing for faster processing times.
- Video Processing Pipeline: A clear video processing pipeline is essential. Break it down into stages: input from an image sensor, image processing using algorithms, and output image handling.
- Massive Parallelism: Take advantage of the FPGA’s ability to handle massive parallelism. This is crucial for processing multiple video frames simultaneously.
- Frame Buffers and Logic Gates: Utilize frame buffers to store intermediate results and logic gates for processing tasks. This setup can improve speed and reliability.
- Intellectual Properties and Machine Learning: Consider incorporating intellectual properties and machine learning algorithms. This integration can enhance auto white balance and motion adaptive capabilities.
By integrating these practices, you’ll elevate your video processing projects and ensure efficient, cutting-edge solutions.