This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
FPGA vs ASIC – What is the Difference? (free calculator)
10/01/2019, hardwarebee
In this article, we will take a look at the features which distinguish FPGA from ASIC and subsequently, what applications and situations these characteristics make either of the two ideal for.
Both FPGA and ASIC are known technologies that have been around for several decades. Many electronic products that we use today, are based on ASICs and many other are based of FPGAs. Both technologies are evolving from year to year and have new offering and new exciting features. Today, FPGAs have more enhanced offering than 10 years ago, they become larger in terms of gate count and today consist today of analog blocks. ASICs have higher gate density and lower power consumption compared to 5 years ago, they a quicker to develop and getting lower in unit cost.
This guide will help you understand the difference between FPGA vs ASIC and better understand how harness those powerful technologies to help you design the best product that meets price, size and power consumption.
Let’s first start with a quick reminder regarding each technology: FPGA vs ASIC.
What is an ASIC?
ASIC stands for Application Specific Integrated Circuit and, as the name suggests, it is a chip which serves the purpose for which it has been designed and cannot be reprogrammed or modified to perform another function or execute another application. ASICs are designed to be used for a specific function which would direct how the chip is programmed in the first place considering its permanency. ASIC are all around us: in your mobile phone, laptop, TV and more. Get price quote for ASIC design services.
What Is an FPGA?
FPGA stands for Field Programmable Gate Array and is essentially a chip which can be programmed and reprogrammed to serve various purposes at any single point in time. A single chip is composed of thousands of units called logic blocks which are linked with programmable interconnects. An FPGA is thus a programmable ASIC. It has a general functionality that can be programmed to a specific desire. Having said that, due to its flexibility it offers a few drawbacks such as higher internal delay, higher cost and limited analog functionality. Get price quote from FPGA design companies.
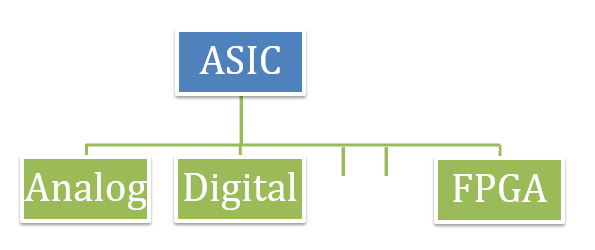
Figure 1: FPGA is one implementation of an ASIC technology
FPGA vs. ASIC Comparison
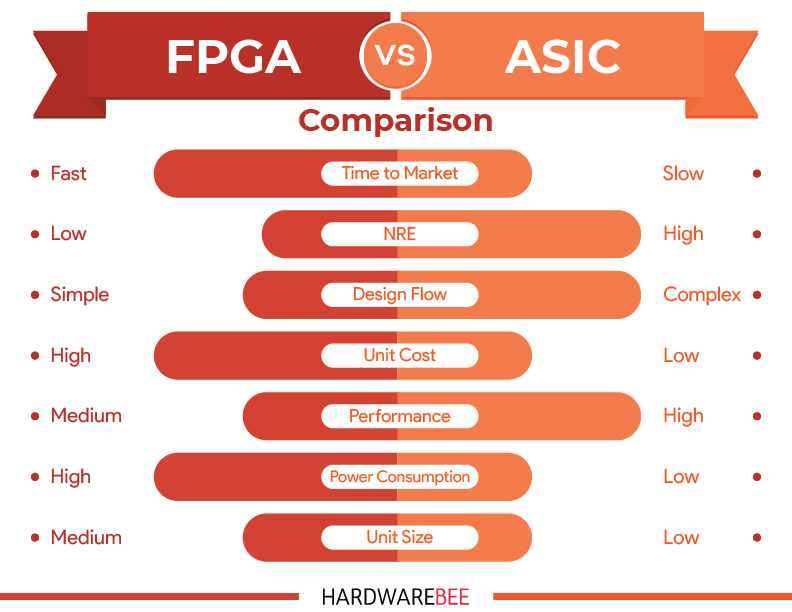
The following list is a comparison between FPGA vs ASIC. Obviously both ASICs and FPGAs excel in various criteria and various applications. We tried to cover as many topics as possible, both technically and commercially, if we missed anything please let us know.
NRE
NRE stands for Non Recurring Engineering costs, a factor which is extremely high when it comes to ASICs and almost non existent in the matter of FPGAs. This means that the NRE costs are higher for ASIC than for FPGA but the total cost gets lower and lower the larger quantities you opt for. FPGA, on the other hand, has little to no NRE costs but can end up costing more as the price of the individual units is higher for FPGA vs ASIC.
Design Flow
Part of the reason why FPGAs have low NRE costs and a faster time to market lies in the fact that its design flow is extremely simple. The reprogrammability and flexibility of the chips is why the flow is simplistic. ASICs are, however, permanent and have a more complex design flow than FPGAs. In fact, ASIC design required dedicated EDA tools that are very costly.
Performance and Efficiency
ASICs edge out FPGAs when it comes to performance because of the lower power consumption and of various possible functionalities which can be layered onto a single chip. FPGA has a rigid internal structure while an ASIC can be layouted to excel in speed or power consumption.
Cost
Despite the higher NRE cost, ASICs are seen to be more cost effective all things considered as compared to FPGAs which are only cost effective when developed in smaller quantities.
Power Consumption
FPGA is a high power consuming chip, making it a more power hungry solution than ASICs which are largely less power consuming and hence, a great solution for battery operated products.
Size
A single unit of an FPGA chip will be relatively larger than an ASIC chip unit. Because FPGA has its internal structure and a certain size that cannot be changed – while ASIC consists of exactly the amount of gates required for the desired application.
Time to Market
FPGA boasts a faster time to market than ASIC. compared to ASIC, FPGAs have shorter design cycles as they are not associated with the need for layouts or back end processes that generally take up much more time when it comes to the development of ASICs. ASICs are also more complex and time consuming because they need to achieve advanced verification whereas FPGA devices are usually already verified and the relevant logic content simply need to be placed onto them.
Configuration
One of the major points that separates these two entities, FPGA vs. ASIC, is the fact that one is reconfigurable and the other is a permanent circuit. ASICs are permanent circuits that cannot be modified once they have been produced. FPGAs are much more flexible in this regard and enable the user to modify parts of it even when it is in use, a feature that makes it a popular choice among individual and fields looking for high velocity, accelerated computing, such as in data centres.
Barrier to Entry
Barrier to entry essentially translates into how difficult it is to acquire and get started using these technologies. When it comes to ASICs, the barrier to entry is a pretty high considering the high upfront NRE costs, complexity of operations, and other necessary investments associated with it. But where ASIC development can cost upward of millions of dollars at times, FPGA development can be started with an amount just under $5000, making it the easier route to take in terms of capital investment.
Unit Cost
When it comes to ASICs, while they may have a high NRE cost, the unit price is relatively low, a factor that makes them suitable for high volume mass production operations. FPGAs have a much higher unit cost compared to the ASIC. Which means that if you are looking to use it for a high volume mass production, you will have to stretch out your budget to a considerable degree to be able to cover the costs.
Operating Frequency
FPGAs have limited operating frequencies, the factor at the expense of which we get the capability to reconfigure the chip. ASICs tend to have the ability to run at higher frequencies as compared to FPGAs at the same node owing to the fact that has been designed to serve one function only and cannot be configured to do something else.
Analog Designs
While FPGAs are reconfigurable, they cannot be used to make analog designs like ASICs which can employ the use of analog hardware such as analog to digital converters, RF blocks (Bluetooth, WiFi) and more.
Figure 2: A Table Showing Comparison between FPGA vs ASIC
FPGA vs ASIC – Applications
The flexibility in the configuration of FPGAs makes it suitable for applications and devices that need to be modified and upgraded frequently as opposed to ASICs that are suited for more permanent applications. This feature is also what makes FPGA the ideal choice for prototyping purposes as the circuit can be modified if there is an error or improvement to be made, something that cannot be done on an ASIC as it is permanent. That is why FPGAs are often used to prototype ASICs before they are actually made. On the other hand, the latter should be the go to choice for large volume productions if configurability is an irrelevant factor.
FPGA vs ASIC – Free Calculator
A free calculator that helps you make the right financial decision to help you choose between ASIC vs FPGA has been developed by HardwareBee team and is available here.