This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
What is the Difference: GDDR5 VS. GDDR6
05/03/2023, hardwarebee
GDDR is an acronym for Graphics Double Data Rate SGRAM. It is the modern version of SGRAM (Synchronous Graphics Random Access Memory).
SGRAM is SDRAM with a few enhancements for graphic applications. DDR’s “double data rate” describes its capability of double data transfer. Data transfers on both the rising and falling edge of the clock signal. It is a type of memory that is specifically designed to support the needs of GPUs and provide them with faster data access. They are used in a wide range of applications, like 3D modeling, video editing, graphic designing, high-performance computing, and in AI applications.
This article will provide a comprehensive overview of GDDR5 VS GDDR6 standards along with the similarities and differences between them. Lets start with describing GDDR5!
GDDR5 Overview
GDDR5 8 GB memory based on 20 nm process node (Image Courtesy Samsung Newsroom)
GDDR5 is a high-end low latency RAM that has a throughput rate of up to 8GB per second. GDDR5 chips are produced by manufacturers, notably Samsung, Hynix, ELPIDA, and Micron. It operates on low power and only requires 1.5V. This feature prevents the system from overheating, and overclocking and reduces manufacturing costs.
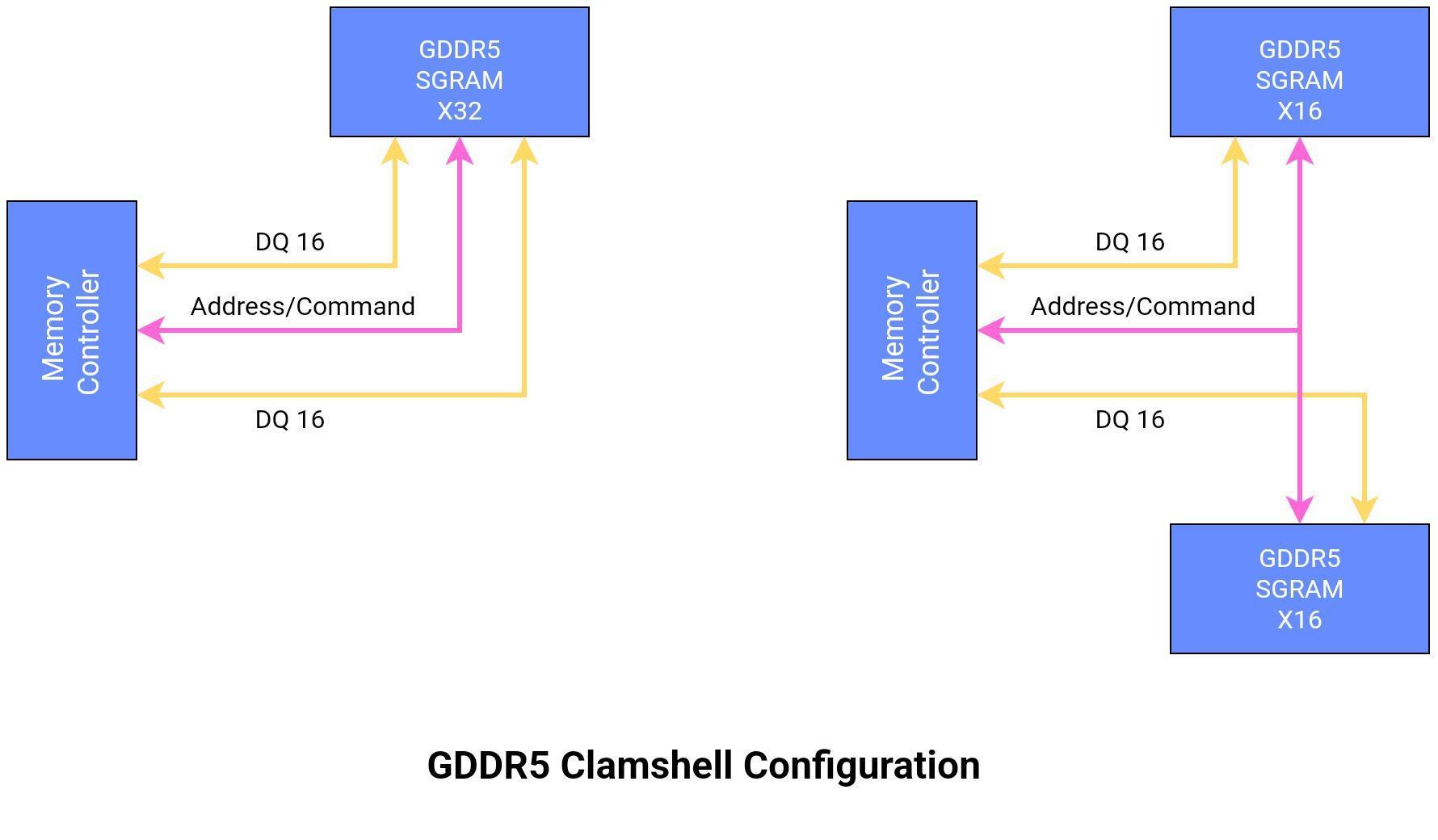
Clamshell Mode
GDDR5 clamshell mode” refers to a specific mode of operation for GDDR5 memory that provides higher memory capacity compared to normal mode. It is a topology that effectively reduces the board space but increases the design complexity. It can operate in an x32 or an x16 mode and allow a clamshell configuration as follows:
Data Rate
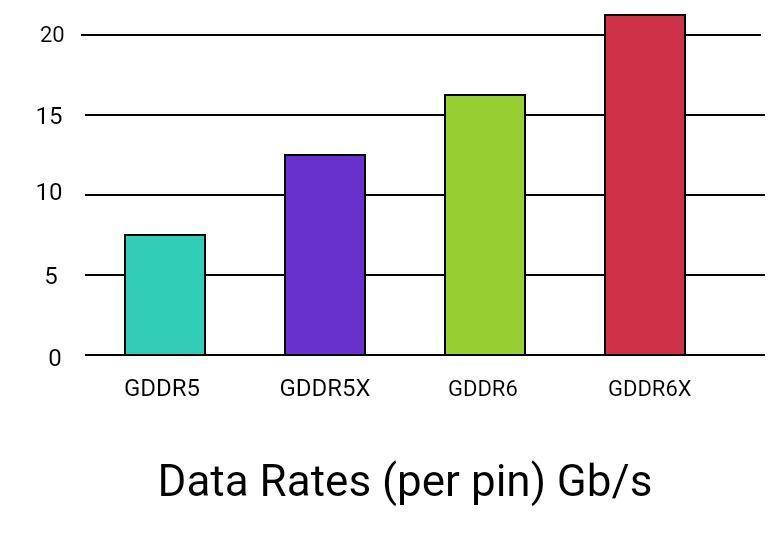
The data rate is an important parameter because it affects the speed at which data can transfer to or from the GPU. A higher data rate means that the memory can transfer data more quickly, which can lead to better performance in high-end graphics applications such as video editing and 3D modeling. A single GDDR5 has a data rate of up to 8 GB/s per pin. It’s worth noting that the GDDR5 memory uses a double data rate (DDR) interface, which means that data is transferred on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal.
Memory Array Prefetch
GDDR5 has an internal 8n prefetch. The term ‘8n prefetch’ means it has an internal data bus that is 8 times wider than the device’s I/O interface. The memory array is a bit slower than the external I/O interface. This 8n prefetch with GDDR5 results in a data throughput of 8 Gb/s at the same internal array cycle time of 1 ns.
Memory Bandwidth
GDDR5 memory bandwidth depends on several factors.
- Increase the clock speed of the memory.
- Another way is to increase the width of the memory bus. This enables the transmission of more data every clock cycle.
- Faster data rates.
GDDR5 has a memory bandwidth that ranges from 64 to 384 GB/s.
Power Consumption
GDDR5 memory was speculated as a power-efficient option for graphics memory, particularly in comparison with older versions of GDDR. It also offers power-down and self-refresh modes for power savings when inactive.
It operates on 1.5 to 1.35 V ranges depending upon the data rates and applications.
Speed
The performance of a GPU is greatly influenced by its speed, which determines how rapidly it can access and transfer data to and from memory.
GDDR5 can handle reading and writing on the same clock cycle, essentially doubling the bus width.
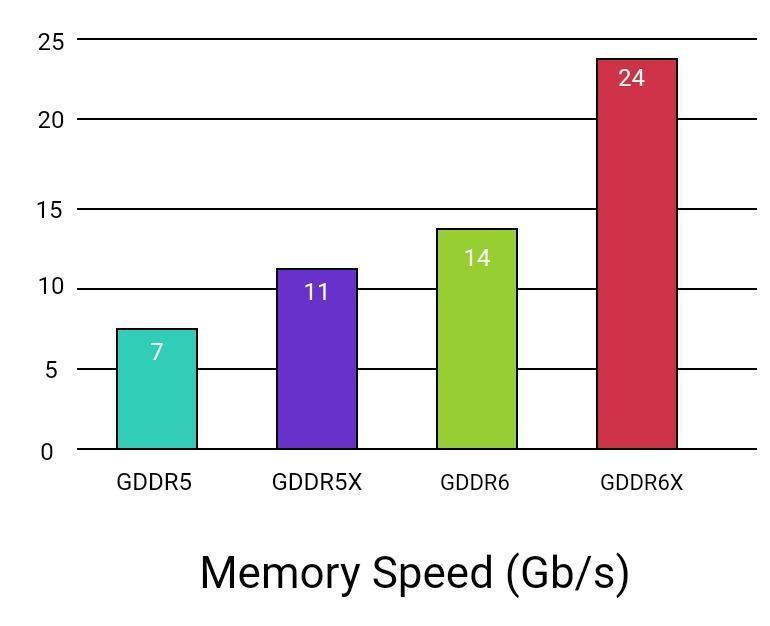
Initially, GDDR5-based systems operated at 3.6 Gb/s. Ever since data rates have improved to 8 GB/s in high-end systems.
GDDR6 Overview
GDDR6 24 GB memory based on 10nm process node (Image Courtesy Samsung News)
Although the GDDR5 has been considered the best choice for most graphic card manufacturers. However, as technology evolves and times change, a new category of graphics memory named GDDR6 has been introduced. It was unveiled in 2019 and used in graphic cards produced by AMD and NVIDIA.
It is the upcoming memory standard for GPU (Graphic Processing Units) and is considered the finest, among the new generation of graphic cards. It is the successor of GDDR5. It incorporates several features from its predecessor GDDR5 and other graphics card standards commonly used in GPUs. Some salient features are higher data rates (up to 21 Gbps), PAM 4 interface, and higher densities.
These chips are produced by several manufacturers, notably Samsung, Hynix, and Micron.
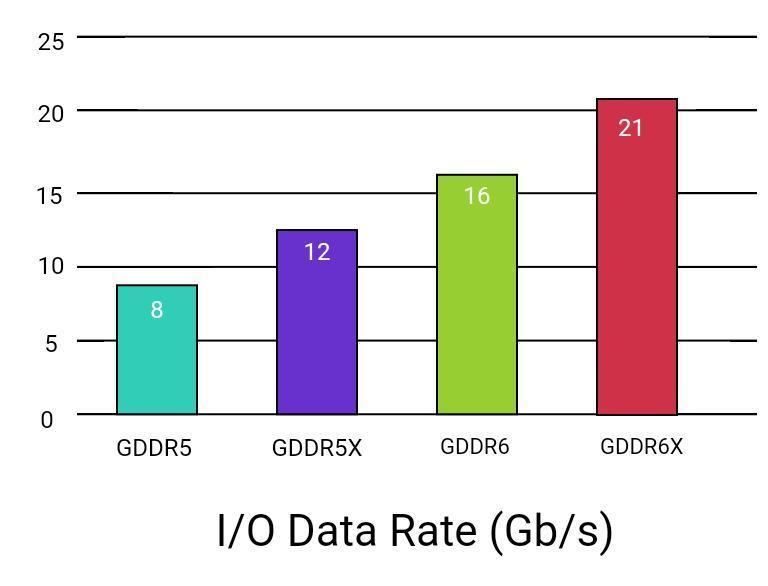
The following chart shows the IO data rate between GDRR5 vs GDRR6:
Burst Length
It offers a burst length of 16. It is doubled as compared to its predecessor. With a longer burst length, the GPUs can access larger chunks of data. It greatly reduces the number of requests for memory required to retrieve a specific amount of data. Hence it enables the memory bus to be used more effectively. Generally, it improves performance however it results in a complex memory controller.
Clamshell Mode
GDDR6 has the same clamshell Mode as GDDR5 but the name has changed from x16 mode to x8 mode. A GDDR6 is segmented into several channels. It has two 16-bit wide channels.
It has a memory system, which is divided into 2 channels. It may support a single device operating in x16 mode or two devices operating in x8 mode.
Data Rate
In this generation, per pin data rate increases up to 16GB/s, which is almost 2 times higher than its predecessor GDDR5. It supports both DDR (double data rate) and QDR (quad data rate) modes. The significant increase in the data rate of GDDR6 is achieved through several optimizations like
- improved signaling scheme.
- Improved memory prefetching.
- higher clock speeds.
GDDR6 memory has a higher bus width and more memory channels compared to GDDR5, which further increases the memory bandwidth and data rate.
Memory Bandwidth
It offers a base clock speed that ranges from 14 Gbps to 16 Gbps and higher memory bandwidth of 192 Gbps.
Memory Array Prefect
Another important upgrade in this generation is the prefetch memory architecture. It has a memory array that is logically divided into two channels.
GDDR 6 has a 16n prefetch memory architecture. It has been divided into two channels (A and B). Both of them have a 32-bit data interface and are completely independent. Having more channels provides a better capability to manage the DRAM. The number of channels doubles as compared to its predecessor. These channels have a read or write memory access of 256 bits (32 bytes wide).
This 16n prefetch with GDDR 6 results in a data throughput of 16 Gb/s at the same internal array cycle time of 1 ns. GDDR6 can fetch twice the amount of data as compared to its predecessor. The following chart show GDDR5 vs GDDR6 memory speed comparison.
Speed
The transfer speed has been significantly improved. It was 8 Gbps in GDDR5. As compared to its predecessor, GDDR5, it offers a significant increase (almost doubled) in memory speed. Currently, it is improved from 8 Gbps to 14-16 Gbps, depending on the specific model and manufacturer.
Power Consumption
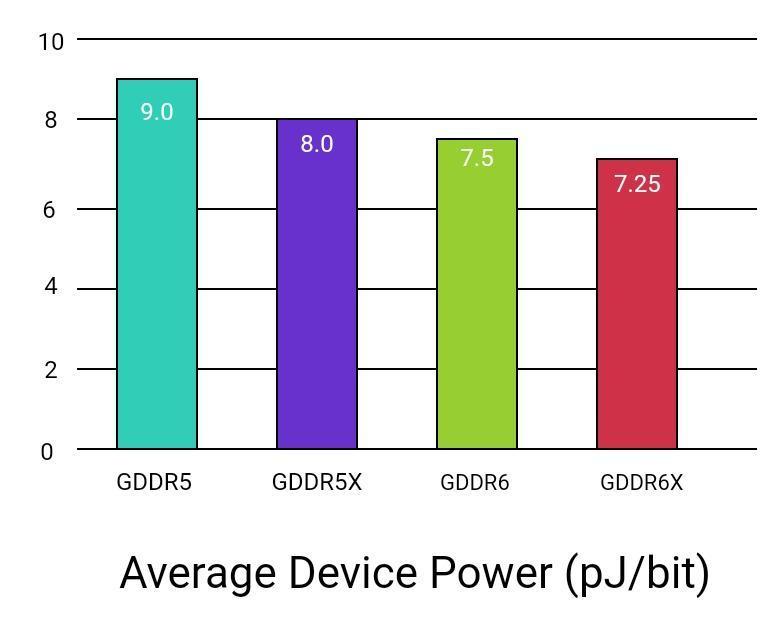
It adopts all the low-power features of its predecessor, which can lead to improved energy efficiency and longer battery life in devices that use it. It is even more power efficient than GDDR5. There is a marginal drop in power consumption by 3% in power per bit transferred. The chart below shows the GDRR6 vs GDRR5 power comparison.
GDRR5 VS GDDR6 Comparison Summary
GDDR5 and GDDR6 are types of graphics memory used in modern computer systems, with GDDR6 being a newer and more advanced version. Here are five key differences between the two:
- Speed: GDDR6 is faster than GDDR5, offering higher memory bandwidths and transfer rates. GDDR6 has a maximum data rate of 16 Gbps, while GDDR5 has a maximum data rate of 8 Gbps.
- Power Efficiency: GDDR6 uses less power than GDDR5, which makes it more power-efficient. This is due to a number of factors, including improved manufacturing processes and better design of the memory modules.
- Density: GDDR6 can achieve higher memory densities than GDDR5, meaning that it can hold more data in the same amount of space. This is achieved through a number of improvements, including better transistor design and more efficient use of memory cells.
- Cost: GDDR6 is generally more expensive than GDDR5 due to its more advanced design and manufacturing processes. However, as GDDR6 becomes more widely adopted, its cost is likely to come down over time.
- Compatibility: GDDR6 is not backwards compatible with GDDR5, meaning that it cannot be used in systems designed to work with GDDR5 memory. This means that upgrading from GDDR5 to GDDR6 may require a complete system overhaul, rather than just a simple memory upgrade.
Overall, GDDR6 represents a significant improvement over GDDR5 in terms of speed, power efficiency, density, and other factors. However, the cost and compatibility issues may make it a less attractive option for some users, particularly those who are looking to upgrade existing systems rather than build new ones from scratch.
The following table shows the difference and similarities between GDDR5 Vs GDDR6:
Survival of the Fittest
This article covers a comprehensive overview of both memory standards. It is concluded that GDDR6 is superior to and more complex than GDDR5. Apart from the dramatic increase in performance, there is also a price increase. It improves on previous GDDR5 designs, which include low power consumption and higher clock speed, and many other notable advancements. To be specific, GDDR6 can also be produced in larger sizes and qualities, like 8GB to 16GB. Whereas GDDR5 was produced in sizes that range from 512MB to 8GB. The new memory standard is capable of processing large amounts of data sets simultaneously, as well as high-performance computing and artificial intelligence-based applications with great speed and efficiency.