This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Introduction to Notch Filter
05/02/2023, hardwarebee
Today, noise and distortion reduction are essential for signals and many other applications. One type of filter used in this field is called a notch filter. Notch filters are designed to remove unwanted noise from a signal and can be used in a variety of contexts. In this article, we will take a look at what notch filters are, how they work, and why they are so useful. We will also examine some of the practical uses for notch filters and discuss how they can benefit your projects.
Figure 1: notch filter
What is Notch Filter?
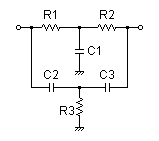
Notch filters are used in a variety of electronic devices to remove a specific range of frequencies from the signal path. The most common type of notch filter is the twin-T notch filter, which uses two inductors and two capacitors to create a band-stop filter. Notch filters are also known as band-stop filters or rejection filters.
One of the most common types of notch filters is the LC (inductor-capacitor) notch filter. This type of filter uses an inductor and a capacitor connected in series or in parallel to create a notch in the frequency response at a specific frequency. The inductor and capacitor are chosen such that the reactance of the inductor and the capacitance are equal at the frequency to be rejected. This creates a zero in the transfer function at that frequency, resulting in a rejection of that frequency.
Another type of notch filter is the digital notch filter. This type of filter uses digital signal processing techniques to create a notch in the frequency response at a specific frequency. Digital notch filters can be implemented using a variety of algorithms such as the Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filter or the Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter. The IIR filter is a recursive filter that uses feedback, while the FIR filter is a non-recursive filter that does not use feedback.
Figure 2: Twin T notch filter
Notch filters are used in a variety of electronic devices, such as radios, televisions, and audio equipment, to remove unwanted noise or interference from the signal path. Notch filters can also be used to improve the sound quality of audio recordings by reducing background noise.
Notch Filter Applications
Notch filters are used in a variety of applications where it is necessary to remove a specific frequency or range of frequencies from a signal. One common application is in audio systems, where notch filters are used to remove unwanted frequencies such as 60 Hz hum from the signal. Notch filters are also used in telecommunications systems to remove interfering signals on specific frequencies, and in instrumentation systems to calibrate sensors by removing known interference signals.
Notch filters can also be used in control systems to remove unwanted frequencies that are causing instability. For example, in a control system for an industrial process, a notch filter can be used to remove a specific frequency component that is causing oscillations in the process.
Notch Filter Characteristics
Notch filters are commonly used in audio applications to reduce unwanted noise, such as hiss, hum, or buzz. Notch filters can also be used to improve the performance of other types of filters by reducing the amount of out-of-band energy that they must process.
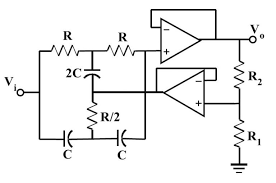
Notch filters are classified as either passive or active. Passive notch filters use only resistors and capacitors, while active notch filters also use one or more operational amplifiers. Active notch filters have the advantage of being able to provide a much sharper cutoff than passive filters, but they require more power and are more expensive.
Figure 3: Active Twin T notch filter
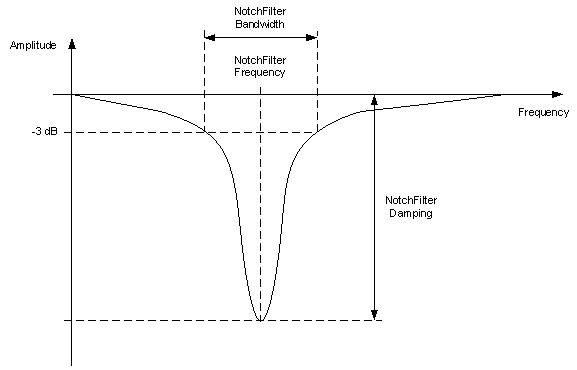
Notch filters are typically designed to have a very steep cutoff slope, often on the order of -60 dB per octave (-20 dB per decade). This means that for each doubling of the input frequency, the output is reduced by 60 dB. The steepness of the cutoff slope is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors used in the filter circuit.
Figure 4: notch filter bandwidth
The quality factor (Q) of a notch filter is a measure of how sharply it attenuates frequencies near the center frequency (fc) of the notch. A high Q filter will have a very sharp attenuation curve, while a low Q filter will have a more gradual attenuation curve.
Notch filter as a Band Pass Filter
A notch filter, also known as a band-stop filter, is a type of filter that is used to reject a specific frequency band while allowing all other frequencies to pass through. The basic principle of a notch filter is to create a frequency response that has a “notch” or a dip in the frequency response at the frequency or frequencies that need to be rejected. The most common type of notch filter is the second-order Butterworth filter. This type of filter has two poles and two zeros. The zeros are located at the center frequency of the notch, and the poles are located at the edge frequencies.
Figure 5: band pass filter
- There are some limitations of notch filters. One of the main limitations is that they can only reject a specific frequency or a narrow frequency band. If the frequency to be rejected is not known, or if the frequency band is too wide, a notch filter may not be the best choice. Additionally, notch filters can introduce distortion to the signal outside of the notch frequency.
- A band-pass filter is a type of filter that rejects frequencies outside of a given range while only allowing frequencies within that range to pass through. It acts as a frequency-selective amplifier, allowing signals within the desired frequency band to pass through while blocking signals outside of the band. Band-pass filters are commonly used in audio processing, telecommunications, and signal processing to isolate or enhance signals of interest while removing unwanted signals.
There are two types of band-pass filters: analog and digital. Analog band-pass filters use electronic components such as inductors and capacitors to create a transfer function with a passband. Digital band-pass filters use mathematical algorithms to create a transfer function that has a passband.
The frequency response of a band-pass filter is characterized by its passband, which is the range of frequencies that are allowed to pass through, and its stopband, which is the range of frequencies that are rejected. The shape of the passband and stopband can be adjusted by changing the values of the components in the filter circuit, or by modifying the coefficients in a digital filter.
Band-pass filters can be designed for different applications by adjusting the width and center frequency of the passband. For example, in audio processing, a band-pass filter can be used to enhance vocals by removing frequencies outside of the vocal range. In telecommunications, a band-pass filter can be used to separate signals in different frequency bands, such as in the case of frequency division multiplexing.
In conclusion, a band-pass filter is a type of filter that allows only a specific range of frequencies to pass through while rejecting frequencies outside of this range. It is commonly used in audio processing, telecommunications, and signal processing to isolate or enhance signals of interest while removing unwanted signals. The frequency response of a band-pass filter is determined by its passband and stopband, which can be adjusted for different applications.
Tunable Notch Filters
Notch filters are also known as band-stop filters or rejection filters. Notch filters are commonly used in audio applications to remove unwanted frequencies, such as 60 Hz power line interference, from a signal.
Notch filters can be tuned to different frequencies by changing the value of the capacitors and inductors used in the filter circuit. The Q factor of a notch filter determines the width of the frequency band that is attenuated by the filter. A higher Q results in a narrower band of frequencies being attenuated.
How to Apply and Implement Notch Filters?
There are a few different ways that notch filters can be applied and implemented, depending on the specific requirements of the situation. In general, though, they can be added to an audio signal path in one of two ways:
- By using an external hardware device that contains the filter circuitry. This is the most common way that notch filters are used in professional audio applications.
- By using software that emulates the behavior of hardware notch filters. This can be a good option for those who do not have access to hardware devices or for those who want to experiment with different filter settings without having to purchase new hardware.
Notch Filter Circuit
A notch filter is an active filter that is used to remove a specific frequency range from a signal. It is a type of band-stop filter. The notch filter is a two-pole filter that uses a capacitor and an inductor to create a resonance at the desired frequency (Figure 5). The resistor in the circuit provides impedance to prevent the current from flowing through the capacitor and inductor.
How do you Make a Notch Filter?
To make a passive notch filter, you will need a resistor and capacitor. First, choose the resistor value. The easiest way to do this is to use a calculator, like the one at http://www.ohmslawcalculator.com/. Once you have the resistor value, put it in series with the capacitor. Then, connect the ground lead of the capacitor to the ground lead of the resistor.
Now you have your basic passive notch filter! You can experiment with different values for the resistor and capacitor to see what effect they have on the signal.