This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Understanding UPS Block Diagram
29/12/2022, hardwarebee
In this article, Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) and its block diagram, application, and types, are introduced. Moreover, it aims to answer frequent questions about UPS for better understanding.
Therefore, the topics of this article are as follows:
- UPS introduction
- UPS benefits
- UPS parts and diagrams
- UPS power range and backup time
What is UPS?
An electronic power supply known as an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) enables some loads to continue operating for at least a short period of time when incoming power is interrupted. In other words, UPS supplies electricity using the energy stored in the battery. As long as utility power flows, it also replenishes and maintains the energy storage The UPS system places between the main power source and the load.
How Does an UPS Work?
In the simplest form, UPS is a supply system that offers uninterrupted power to the AC load by converting DC into AC. UPS differs from an emergency power supply system or a standby generator, as it can protect devices from power outages by one or more connected batteries. The battery run time is relatively short, typically 5 to 15 minutes, but it is long enough to bring the auxiliary power supply online or protect devices from shutting down.
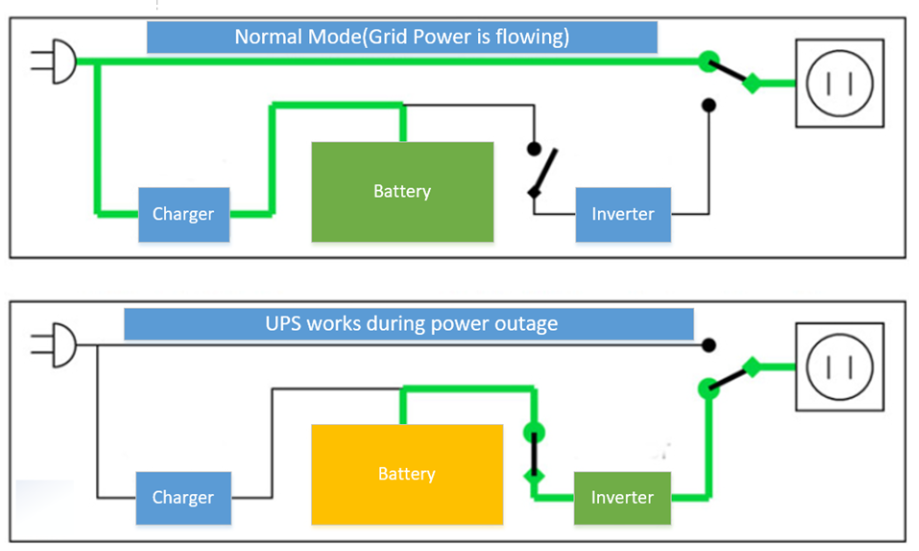
In normal operating conditions, the current is drawn from the AC main power supply or grid, while UPS provides load current in case of a power outage. Here the battery is used as the backup source to deliver power to the load in case of power failure.
Benefits of Using UPS
The main task of the UPS is to keep power flowing when the main power is gone. However, the UPS can regulate and stabilize the grid power, preventing noise and disturbances, especially for sensitive equipment. The electronic filters in the UPS prevent the grid voltage fluctuations and noise from harming the consumer devices. Furthermore, they can be protected against lightning and high voltage.
Some types of UPSs have special features. For example, some UPSs have warning alarms when errors or overloads occur or computer control software to save the information and turn off the computer, etc.
Offline UPS is usually used for laptop and desktop computers, POS systems, and primary electronic equipment. Furthermore, there are enormous fields that require a continuous source of power without any interruption. Some of these fields are:
- Medical care systems,
- Safety monitoring systems,
- IT and networking fields,
- Data centers,
- Elevators,
- Industrial or home fridges during hot seasons.
UPS Types
Generally, UPSs can be categorized into the following types:
- Offline UPS: Offline: Offline UPS types are activated only when the main power is gone. In this type, the UPS is connected directly to the consumer load. However, the offline type does not have an acceptable quality for the output power, and its maximum power is limited.
- Online UPS: If you also want the proper and suitable output power, the online type can be a good option for you. In online types, the inverter can charge batteries and provide output power simultaneously. It means the grid power is converted into direct current by a rectifier. Then it is converted into alternating current by the inverter section and is ready to use by consumer loads. This conversion can protect consumer devices from volatile grid voltage.
- Line interactive UPS: In this type, the inverter always charges the battery in the normal voltage range. Nevertheless, as soon as the input voltage goes beyond or below the normal range, UPS is activated, and supplies the consumer load from the batteries and prevents damage to connected devices. The interactive line type is mostly used in network equipment.
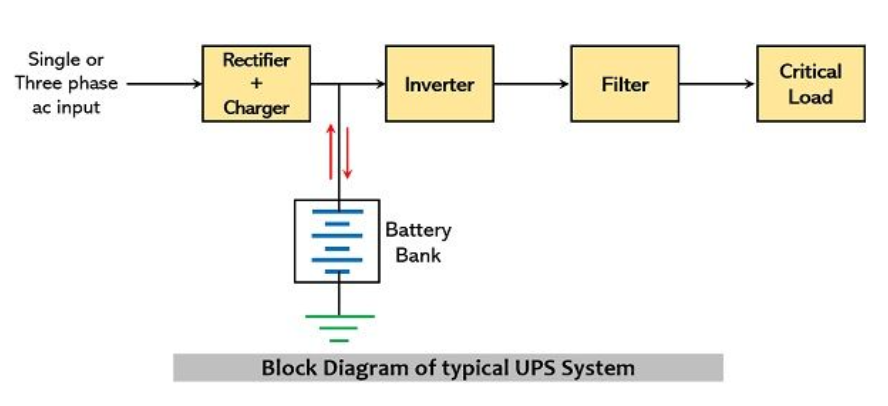
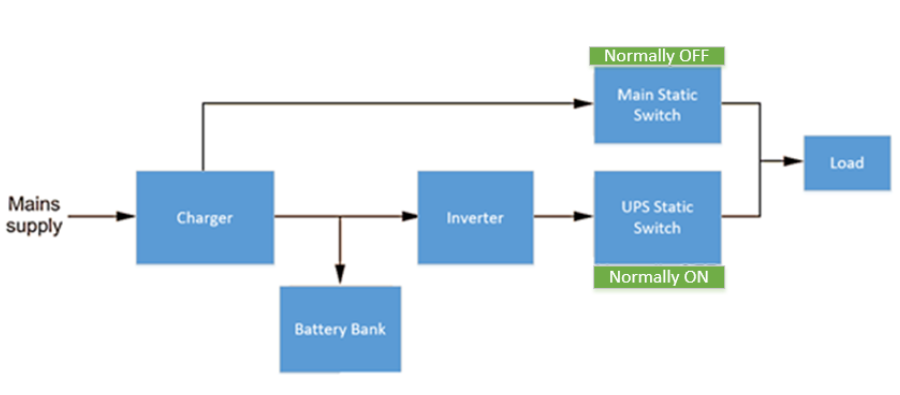
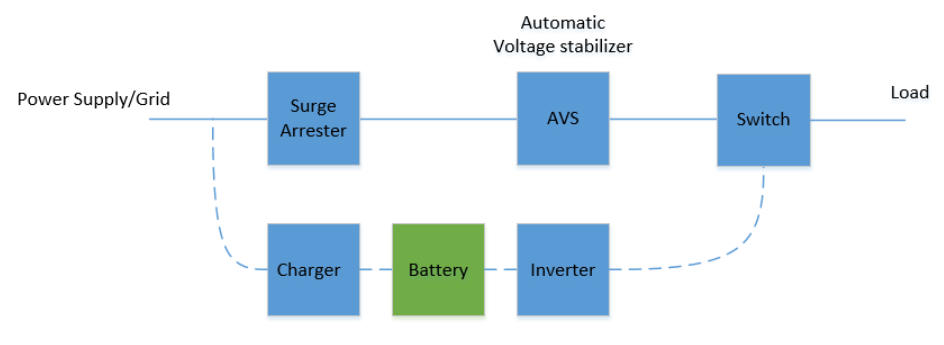
UPS Block Diagram
A typical UPS block diagram is shown in block diagram in the picture below:
However, there are a few differences in block diagrams between types of UPS.
Offline UPS Block Diagram
Offline UPS device’s major components include a rectifier, inverter, battery bank, filter circuit, and critical load. A single-phase or a three-phase input signal is provided as input to the rectifier.
In normal operating conditions, the current is drawn from the ac main power supply or grid, while the backup source provides current in case of a power outage. Here battery is used as the backup source to deliver power to the load in case of power failure.
- Charger: This block rectifies the input AC and charges the batteries. The charger block unit involves an EMI filter, rectifier, and DC filter. Here is a small explanation of how each sub-component works:
- EMI filter: this unit reduces noises and disturbances from the input AC signal.
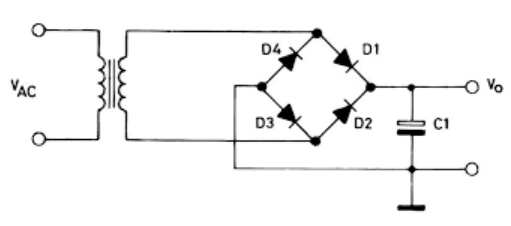
- Rectifier: this unit converts AC current to DC current.
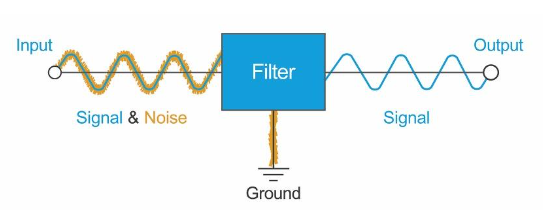
- DC filter: The rectifier’s needed output voltage is unidirectional and does not change concerning time. It has an average or DC value on which AC components of different frequencies are superimposed (mixed). These undesired AC components mixed in DC are called Ripples. Therefore, filter circuits are necessary for DC Regulation. Thus, this part task reduces the negative ripple effect and makes the output current much more in DC shape.
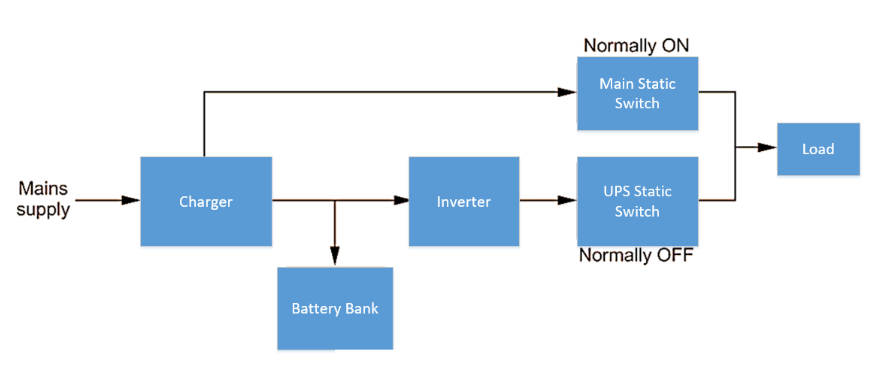
- Static switch: Static Switches are designed to connect or disconnect the load to or from the supply, respectively, without the existence of moving parts.
- Inverter: DC to AC inverters are designed to change a DC (direct current) power supply to an AC (alternating current) power supply.
- Battery bank: An assemblage of one or more individual batteries used to store energy in electrochemical form is referred to as a battery bank.
- Load: sensitive and critical loads selected by the user
Online UPS Block Diagram
In online UPS, the load draws power from the battery bank and main power supply simultaneously. Because the load initially receives electricity from the main power supply but switches seamlessly to the battery backup in the event of a power outage, the supply delivered to the load is uninterruptible. This is the difference between online and offline UPSs.
- Advantages of On-line UPS
- It offers continuous power flow with complete isolation from the main power supply or grid ac input to the end user,
- Constantly uninterrupted electricity is given to the load,
- Main power supply failure (outage) cannot change the operation mode,
- The transfer time is negligible due to the always-on condition,
- Wide range of input voltage
- Disadvantages of On-line UPS
- Due to Continuous on-mode, it generates more heat. Hence, a large heat sink is required.
- It has a Complex design.
- It is much more expensive than offline UPS.
- Higher power loss (since the inverter is always on, the overall efficiency of the device is reduced).
Line Interactive UPS Block Diagram
Line interactive technology UPSs are being used in places where we have sensitive and expensive devices and equipment because electrical fluctuations will lead Sensitive electrical devices to fail. Thus, they should not be subject to fluctuations or noises. Line interactive UPSs are usually used for network equipment. For instance, line interactive UPS is utilized for departmental servers, websites, and small company servers. The line interactive design is a combination of offline & online schematic. In line with interactive design, the inverter plays a dual role. first, it charges the battery when the main power supply is flowing. Second, it regulates the output voltage and works as a normal inverter in the absence of the main power supply.
Line-interactive UPS can remove slight fluctuations in power flow, such as a decrease or increase in voltage level, without switching to the battery. Line Interactive UPS provides more power protection and reliability than basic Offline designs. The difference is the addition of a tap-changing transformer, voltage regulator, or Automatic voltage stabilizer. This tap-changing transformer regulates the voltage by changing the tap depending on the input voltage. Additional filtering is provided in this UPS, resulting in a lower transient loss. The block diagram is shown below.
The interesting thing about Line Interactive UPS is that using too much battery can affect greatly impact on its lifetime. Moreover, Line-Interactive inverters are usually designed to resupply load current by main supply power in case of failure in UPS.
- Advantages of Line-interactive UPS
- High reliability and high efficiency,
- Lower costs than On-line UPS,
- High power supply,
- Noise and fluctuation filtering
- Better protection than Offline UPS
- Disadvantages of Line-interactive UPS
- Line interactive UPS cannot fully filter noise and fluctuation with low power demands (like 5KA and below),
- Output frequency depends on the input frequency.
- Line interactive UPS has not power factor correction circuit.
UPS output power range and back up time
UPSs have different output power, which is calculated and designed according to the amount of the connected load. Usually, the UPS output power is shown in the volt-ampere (VA) unit. The common UPS output powers in the market are 600VA, 1kVA, 1.5kVA, 2kVA, 6kVA, 10kVA, 15kVA, and 20kVA. Backup time is the amount of time that UPS can supply the connected load/loads and depends on how many batteries UPS has.